-
파이썬 정렬 알고리즘 모음 + 속도 테스트컴퓨터/파이썬 2020. 8. 10. 16:34728x90반응형
15개 정렬 알고리즘 소개
0. 정렬 알고리즘 속도 테스트 코드
big-O-calculator 이용 @설치 링크
import bisect import heapq import inspect from random import randint, shuffle from statistics import mean from timeit import default_timer, repeat import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from bigO import BigO from win10toast import ToastNotifier # timeit.repeat 이용 def runAlgorithm(algorithm, array, timeResults): setup_code = f"from __main__ import {algorithm}" if algorithm != "sorted" else "" stmt = f"{algorithm}({array})" times = repeat(setup=setup_code, stmt=stmt, repeat=3, number=5) timeResults[algorithm] = round(min(times), 5) print(f"def: {algorithm}(), 최소 실행 시간: {mean(times)/5:.5f}초") # timeit.default_timer() 직접 계산 def runAlgorithm2(algorithm, array, timeResults): tot = 0.0 # print("정렬 전", array) t0 = default_timer() if algorithm == "sorted": result = list(sorted(array)) else: result = globals()[algorithm](array) t1 = default_timer() # print("정렬 후", result) print(f"{algorithm}() 정렬 결과 : {list(sorted(array)) == result}") tot += t1 - t0 timeResults[algorithm] = round(tot, 5) print(f"def: {algorithm}(), 최소 실행 시간: {tot:.5f}초") # 추천 def runAlgorithm3(algorithm, array, timeResults): lib = BigO() # print("정렬 전", array) testArray = array.copy() time, result = lib.runtime(algorithm, testArray, epoch=3, prtResult=False) # 3회 평균 print(f"{algorithm.__name__}(array) 정렬 결과 : {sorted(testArray) == result}") # print("정렬 후", result) timeResults[algorithm] = round(time, 5) def retrieve_name(var): # 변수 이름 가져오기 callers_local_vars = inspect.currentframe().f_back.f_locals.items() return [var_name for var_name, var_val in callers_local_vars if var_val is var] def saveResultAsPNG(timeResults, name, title): # 그래프 저장 times = [] labels = [] # 값에 따른 정렬 for key, value in sorted(timeResults.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]): times.append(value) labels.append(key.__name__) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8), dpi=80) # 800x640 ax = plt.subplot() ax.set_xticks(range(len(times))) ax.set_xticklabels(labels, rotation=20) plt.bar(range(len(times)), times) plt.title(f"{title} (length: {ARRAY_LENGTH})") plt.ylabel("Times (sec)") plt.savefig(name) def switch(name): return { "array1": "Random", "array2": "Decending sorted", "array3": "Ascending sorted", "array4": "Partially sorted", "array5": "Ksorted", "array6": "All equal", "array7": "Almost equal", "array8": "Hole", }.get(name, "") toaster = ToastNotifier() toaster.show_toast("Sorting", "Sorting algorithms are running", icon_path="D:\DEV\Code\Python\img\python.ico", duration=10) # setrecursionlimit(ARRAY_LENGTH) if __name__ == "__main__": lib = BigO() ARRAY_LENGTH = 5000 # 배열 크기 # Random array1 = lib.genRandomArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # Decending sorted array2 = lib.genReversedArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # Ascending sorted array3 = lib.genSortedArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # Partially sorted array4 = lib.genPartialArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # Ksorted array5 = lib.genKsortedArray(ARRAY_LENGTH, ARRAY_LENGTH.bit_length()) # Equal array6 = lib.genEqualArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # Almost Equal array7 = lib.genAlmostEqualArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # Hole array8 = lib.genHoleArray(ARRAY_LENGTH) # for 1, 2 run() times = {"sorted": 0, "countSort": 0, "introSort": 0, "timSort": 0, "quickSort": 0, "mergeSort": 0, "heapSort": 0, "smoothSort": 0, "pancakeSort": 0, "insertSort": 0, "bubbleSort": 0, "gnomeSort": 0} run = { sorted: 0, countSort: 0, introSort: 0, timSort: 0, quickSort2: 0, mergeSort: 0, heapSort: 0, smoothSort: 0, pancakeSort: 0, insertSort: 0, insertSort2: 0, binaryInsertSort: 0, bubbleSort: 0, goSort: 0, } test = [array1, array2, array3, array4, array5, array6, array7, array8] for index in range(len(test)): for function in run.keys(): testArray = test[index].copy() # Shallow Copy runAlgorithm3(algorithm=function, array=testArray, timeResults=run) name = switch(retrieve_name(test[index])[0]) saveResultAsPNG(run3, f"array{index + 1}.png", name) # runAlgorithm(algorithm="bogoSort", array=testArray, timeResults=times) toaster.show_toast( "Sorting", "Measurements done", icon_path=None, duration=5, threaded=False )1. Bubble Sort (버블 정렬)
def bubbleSort(array): # in-place | stable """ Best : O(n) | O(1) Space Average : O(n^2) | O(1) Space Worst : O(n^2) | O(1) Space """ isSorted = False counter = 0 n = len(array) - 1 while not isSorted: isSorted = True for i in range(n - counter): if array[i] > array[i + 1]: array[i], array[i + 1] = array[i + 1], array[i] isSorted = False counter += 1 return array2. Binary Insertion Sort (바이너리 삽입 정렬)
def binarySearch(array, item, start, end): if start == end: if array[start] > item: return start else: return start + 1 if start > end: return start mid = (start + end) // 2 if array[mid] < item: return binarySearch(array, item, mid + 1, end) elif array[mid] > item: return binarySearch(array, item, start, mid - 1) else: return mid def binaryInsertSort(array): for index in range(1, len(array)): value = array[index] pos = binarySearch(array, value, 0, index - 1) array = array[:pos] + [value] + \ array[pos:index] + array[index + 1:] return array3. Bogo Sort
def bogoSort(array): # in-place """ Best Case Complexity: O(n) Average Case Complexity: O(n(n-1)!) Worst Case Complexity: O(∞) """ def is_sorted(array): i = 0 while i+1 < len(array): if array[i] > array[i+1]: return False i += 1 return True while not is_sorted(array): shuffle(array) return array4. Brick Sort (Odd-Even Sort) 홀짝 정렬
def brickSort(array): """ Odd-Even Sort""" isSorted = False n = len(array) - 1 while not isSorted: isSorted = True for i in range(1, n, 2): if array[i] > array[i + 1]: array[i], array[i + 1] = array[i + 1], array[i] isSorted = False for i in range(0, n, 2): if array[i] > array[i + 1]: array[i], array[i + 1] = array[i + 1], array[i] isSorted = False return array5. Count Sort
def countSort(arr): # stable # Time Complexity : O(n) | Space Complexity : O(n) minValue = min(arr) maxValue = max(arr) - minValue buckets = [0 for _ in range(maxValue + 1)] for i in arr: buckets[i - minValue] += 1 index = 0 for i in range(len(buckets)): while buckets[i] > 0: arr[index] = i + minValue index += 1 buckets[i] -= 1 return arr6. Comb Sort (빗 정렬)
def combSort(array): gap = n = len(array) swapped = True while gap > 1 or swapped: swapped = False gap = int(gap * 10 / 13) if gap < 1: swapped = False gap = 1 for i in range(n - gap): if array[i] > array[i + gap]: array[i], array[i + gap] = array[i + gap], array[i] swapped = True return array7. Gnome Sort
def gnomeSort(array): # in-place | stable ''' Best : O(n) Time | O(1) Space Average : O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space Worst : O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space ''' index = 0 while index < len(array): if index == 0: index = index + 1 if array[index] >= array[index - 1]: index = index + 1 else: array[index], array[index-1] = array[index-1], array[index] index = index - 1 return array8. Heap Sort (힙 정렬)
def heapSort(arr): # in-place | not-stable # Time Complexity O(nlogn) | Space Complexity O(1) def heapify(arr, n, i): # Max Heap largest = i # 트리에서 가장 큰 값 찾기 l = 2 * i + 1 # Left Node r = 2 * i + 2 # Right Node if l < n and arr[i] < arr[l]: largest = l if r < n and arr[largest] < arr[r]: largest = r # root가 최대가 아니면 # 최대 값과 바꾸고, 계속 heapify if largest != i: arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] heapify(arr, n, largest) n = len(arr) for i in range(n // 2, -1, -1): heapify(arr, n, i) for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1): arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] # Heapify root element heapify(arr, i, 0) return arr # 파이썬 heappop, heapify 소스 이용 def heapSort2(iterable): # in-place | not-stable # Time Complexity O(nlogn) # Using Python source at # https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/975d10a4f8f5d99b01d02fc5f99305a86827f28e/Lib/heapq.py def heappop(heap): """Pop the smallest item off the heap, maintaining the heap invariant.""" lastelt = heap.pop() # raises appropriate IndexError if heap is empty if heap: returnitem = heap[0] heap[0] = lastelt _siftup(heap, 0) return returnitem return lastelt def _siftup(heap, pos): endpos = len(heap) startpos = pos newitem = heap[pos] # Bubble up the smaller child until hitting a leaf. childpos = 2 * pos + 1 # leftmost child position while childpos < endpos: # Set childpos to index of smaller child. rightpos = childpos + 1 if rightpos < endpos and not heap[childpos] < heap[rightpos]: childpos = rightpos # Move the smaller child up. heap[pos] = heap[childpos] pos = childpos childpos = 2 * pos + 1 # The leaf at pos is empty now. Put newitem there, and bubble it up # to its final resting place (by sifting its parents down). heap[pos] = newitem _siftdown(heap, startpos, pos) def _siftdown(heap, startpos, pos): newitem = heap[pos] # Follow the path to the root, moving parents down until finding a place # newitem fits. while pos > startpos: parentpos = (pos - 1) >> 1 parent = heap[parentpos] if newitem < parent: heap[pos] = parent pos = parentpos continue break heap[pos] = newitem def heapify(x): """Transform list into a heap, in-place, in O(len(x)) time.""" n = len(x) # Transform bottom-up. The largest index there's any point to looking at # is the largest with a child index in-range, so must have 2*i + 1 < n, # or i < (n-1)/2. If n is even = 2*j, this is (2*j-1)/2 = j-1/2 so # j-1 is the largest, which is n//2 - 1. If n is odd = 2*j+1, this is # (2*j+1-1)/2 = j so j-1 is the largest, and that's again n//2-1. for i in reversed(range(n // 2)): _siftup(x, i) return x h = heapify(iterable) return [heappop(h) for _ in range(len(h))]heapSort2를 파이썬 소스에서 따와서 사용해보았는데
전체적으로 heapSort2가 237% 가량 빠르다.
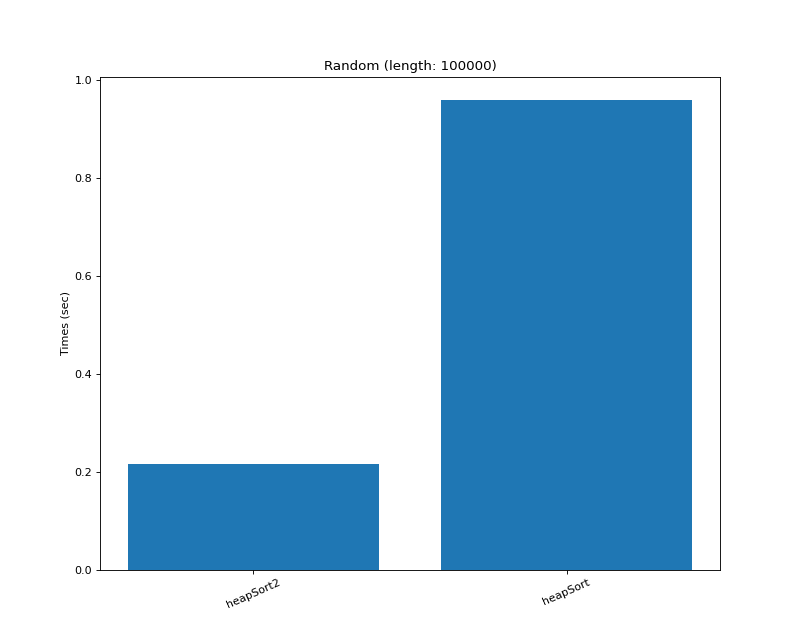
9. Insertion Sort (삽입 정렬)
def insertSort(array): # in-place | stable ''' Best O(n) Time | O(1) Space Average O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space Worst (On^2) Time | O(1) Space ''' for i in range(len(array)): j = i toChange = array[i] while (j != 0 and array[j - 1] > toChange): array[j] = array[j - 1] j -= 1 array[j] = toChange return array # 좀 더 간단히 def insertSort(array): for i in range(1, len(array)): j = i while j > 0 and array[j] < array[j - 1]: array[j], array[j - 1] = array[j - 1], array[j] j -= 1 return array9-1. Insertion Sort 최적화
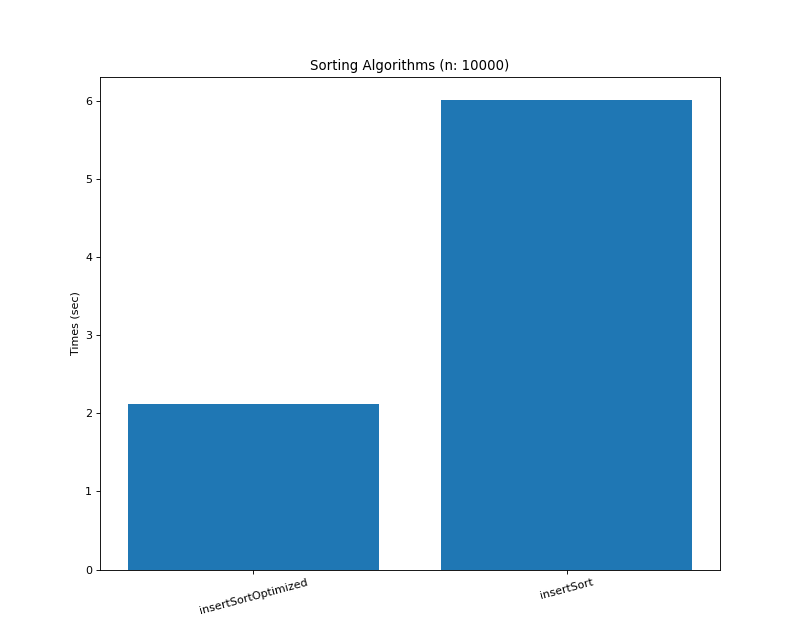
정렬된 케이스빼곤 3~5배 정도 빠름
def insertSortOptimized(array): for i in range(1, len(array)): if array[i] >= array[i - 1]: continue for j in range(i): if array[i] < array[j]: array[j], array[j + 1 : i + 1] = array[i], array[j:i] break return array10. Introspective Sort (내성 정렬)
heap Sort + Insertion Sort + Quick Sort
https://choiseokwon.tistory.com/209
def introSort(array): # in-place | not-stable # Time Complexity O(nlogn) | Space Complexity O(logn) maxDepth = 2 * (len(array).bit_length() - 1) sizeThreshold = 16 return introSortHelper(array, 0, len(array), sizeThreshold, maxDepth) def introSortHelper(array, start, end, sizeThreshold, depthLimit): def medianOf3(array, lowIdx, midIdx, highIdx): if (array[lowIdx] - array[midIdx]) * (array[highIdx] - array[lowIdx]) >= 0: return array[lowIdx] elif (array[midIdx] - array[lowIdx]) * (array[highIdx] - array[midIdx]) >= 0: return array[midIdx] else: return array[highIdx] def getPartition(array, low, high, pivot): i = low j = high while True: while (array[i] < pivot): i += 1 j -= 1 while (pivot < array[j]): j -= 1 if i >= j: return i array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i] i += 1 while(end - start > sizeThreshold): if depthLimit == 0: return heapSort(array) depthLimit -= 1 median = medianOf3(array, start, start + ((end - start) // 2) + 1, end - 1) p = getPartition(array, start, end, median) introSortHelper(array, p, end, sizeThreshold, depthLimit) end = p return insertSort(array, start, end) def insertSort(array, begin=0, end=None): # in-place | stable ''' Best O(n) Time | O(1) Space Average O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space Worst (On^2) Time | O(1) Space ''' if end == None: end = len(array) for i in range(begin, end): j = i toChange = array[i] while (j != begin and array[j - 1] > toChange): array[j] = array[j - 1] j -= 1 array[j] = toChange return array11. Merge Sort (병합 정렬)
def mergeSort(array): # stable """ Best : O(nlogn) Time | O(n) Space Average : O(nlogn) Time | O(n) Space Worst : O(nlongn) Time | O(n) Space """ def mergeHelper(main, startIdx, endIdx, aux): if startIdx == endIdx: return middleIdx = (startIdx + endIdx) // 2 mergeHelper(aux, startIdx, middleIdx, main) mergeHelper(aux, middleIdx + 1, endIdx, main) merge(main, startIdx, middleIdx, endIdx, aux) def merge(main, startIdx, middleIdx, endIdx, aux): k = startIdx i = startIdx j = middleIdx + 1 while i <= middleIdx and j <= endIdx: if aux[i] <= aux[j]: main[k] = aux[i] i += 1 else: main[k] = aux[j] j += 1 k += 1 while i <= middleIdx: main[k] = aux[i] i += 1 k += 1 while j <= endIdx: main[k] = aux[j] j += 1 k += 1 if len(array) <= 1: return array aux = array[:] mergeHelper(array, 0, len(array) - 1, aux) return array12. Pancake Sort (팬케이크 정렬)
def pancakeSort(array): # in-place | not-stable # O(n^2) Time | O(N) Space if len(array) <= 1: return array for cur in range(len(array), 1, -1): # Finding index of maximum number in arr index_max = array.index(max(array[0:cur])) if index_max+1 != cur: # Needs moving if index_max != 0: # reverse from 0 to index_max array[:index_max+1] = reversed(array[:index_max+1]) # Reverse list array[:cur] = reversed(array[:cur]) return array13. Quick Sort (빠른 정렬)
빠른 정렬은 pivot 선택 방식에 따라 속도 차이가 난다.
보통, low=0, mid=(high-low)//2, end=len(array) -1을 사용하지만, 이 방식은 정렬된 배열에서 속도가 매우 떨어진다.
최적화 방법1)
pivot 선택 랜덤 getMedian(randint[len(array)-1], randint[len(array)-1], randint[len(array)-1])
위 방식은, $1.2nlogn$ 비교를 하게 된다.
def quickSort(array): # in-place | not-stable ''' Best : O(nlogn) Time | O(logn) Space Average : O(nlogn) Time | O(logn) Space Worst : O(n^2) Time | O(logn) Space ''' if len(array) <= 1: return array smaller, equal, larger = [], [], [] pivot = array[randint(0, len(array)-1)] for x in array: if x < pivot: smaller.append(x) elif x == pivot: equal.append(x) else: larger.append(x) return quickSort(smaller)+equal+quickSort(larger) # Hoare + Tail recursive + insertion sort def quickSort2(array, low=0, high=None): def insertSort(array, low=1, high=None): if high is None: high = len(array) for i in range(low, high): j = i while j > 0 and array[j] < array[j - 1]: array[j], array[j - 1] = array[j - 1], array[j] j -= 1 return array if high is None: high = len(array) - 1 while low < high and high - low > 16: q = partition(array, low, high) quickSort2(array, low, q) low = q + 1 return insertSort(array, low + 1, high + 1) # Hoare's partition scheme def partition(array, low, high): pivot = array[(high + low) // 2] # pivot = array[randint(low, high)] i = low - 1 j = high + 1 while True: i += 1 while array[i] < pivot: i += 1 j -= 1 while array[j] > pivot: j -= 1 if i >= j: return j array[i], array[j] = array[j], array[i] # QuickSort 단순 버전 def quickSortSimple(arr): if len(arr) <= 1: return arr else: return quickSortSimple([x for x in arr[1:] if x < arr[0]]) + [arr[0]] + quickSortSimple([x for x in arr[1:] if x >= arr[0]])14. Selection Sort (선택 정렬)
def selectionSort(array): # in-place, unstable ''' Best : O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space Average : O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space Worst : O(n^2) Time | O(1) Space ''' for currentIdx in range(len(array) - 1): smallestIdx = currentIdx for i in range(currentIdx + 1, len(array)): if array[smallestIdx] > array[i]: smallestIdx = i array[currentIdx], array[smallestIdx] = array[smallestIdx], array[currentIdx] return array15. Tim Sort
import bisect def timSort(lst): # in-place | stable """ Python sort(), sorted() implementation from https://github.com/hu-ng/timsort/blob/master/timsort.py Best : O(n) Time | O(n) Space Average : O(nlogn) Time | O(n) Space Worst : O(nlogn) Time | O(n) Space """ def reverse(lst, s, e): """Reverse the order of a list in place Input: s = starting index, e = ending index""" while s < e and s != e: lst[s], lst[e] = lst[e], lst[s] s += 1 e -= 1 def make_temp_array(lst, s, e): """From the lst given, make a copy from index s to index e""" array = [] while s <= e: array.append(lst[s]) s += 1 return array def merge_compute_minrun(n): """Returns the minimum length of a run from 23 - 64 so that the len(array)/minrun is less than or equal to a power of 2.""" r = 0 while n >= 32: r |= n & 1 n >>= 1 return n + r def count_run(lst, s_run): """Count the length of one run, returns starting/ending indices, a boolean value to present increasing/decreasing run, and the length of the run""" increasing = True # If count_run started at the final position of the array if s_run == len(lst) - 1: return [s_run, s_run, increasing, 1] else: e_run = s_run # Decreasing run (strictly decreasing): if lst[s_run] > lst[s_run + 1]: while lst[e_run] > lst[e_run + 1]: e_run += 1 if e_run == len(lst) - 1: break increasing = False return [s_run, e_run, increasing, e_run - s_run + 1] # Increasing run (non-decreasing): else: while lst[e_run] <= lst[e_run + 1]: e_run += 1 if e_run == len(lst) - 1: break return [s_run, e_run, increasing, e_run - s_run + 1] def bin_sort(lst, s, e, extend): """Binary insertion sort, assumed that lst[s:e + 1] is sorted. Extend the run by the number indicated by 'extend'""" for i in range(1, extend + 1): pos = 0 start = s end = e + i # Value to be inserted value = lst[end] # If the value is already bigger than the last element from start -> end: # Don't do the following steps if value >= lst[end - 1]: continue # While-loop does the binary search while start <= end: if start == end: if lst[start] > value: pos = start break else: pos = start + 1 break mid = (start + end) // 2 if value >= lst[mid]: start = mid + 1 else: end = mid - 1 if start > end: pos = start # 'Push' the elements to the right by 1 element # Copy the value back the right position. for x in range(e + i, pos, -1): lst[x] = lst[x - 1] lst[pos] = value def gallop(lst, val, low, high, ltr): """Find the index of val in the slice[low:high]""" if ltr == True: # Used for merging from left to right # The index found will be so that every element prior # to that index is strictly smaller than val pos = bisect.bisect_left(lst, val, low, high) return pos else: # Used for merging from right to left # The index found will be so that every element from # that index onwards is strictly larger than val pos = bisect.bisect_right(lst, val, low, high) return pos def merge(lst, stack, run_num): """Merge the two runs and update the remaining runs in the stack Only consequent runs are merged, one lower, one upper.""" # Make references to the to-be-merged runs run_a = stack[run_num] run_b = stack[run_num + 1] # Make a reference to where the new combined run would be. new_run = [run_a[0], run_b[1], True, run_b[1] - run_a[0] + 1] # Put this new reference in the correct position in the stack stack[run_num] = new_run # Delete the upper run of the two runs from the stack del stack[run_num + 1] # If the length of run_a is smaller than or equal to length of run_b if run_a[3] <= run_b[3]: merge_low(lst, run_a, run_b, 7) # If the length of run_a is bigger than length of run_b else: merge_high(lst, run_a, run_b, 7) def merge_low(lst, a, b, min_gallop): """Merges the two runs quasi in-place if a is the smaller run - a and b are lists that store data of runs - min_gallop: threshold needed to switch to galloping mode - galloping mode: uses gallop() to 'skip' elements instead of linear merge""" # Make a copy of the run a, the smaller run temp_array = make_temp_array(lst, a[0], a[1]) # The first index of the merging area k = a[0] # Counter for the temp array of a i = 0 # Counter for b, starts at the beginning j = b[0] gallop_thresh = min_gallop while True: a_count = 0 # number of times a win in a row b_count = 0 # number of times b win in a row # Linear merge mode, taking note of how many times a and b wins in a row. # If a_count or b_count > threshold, switch to gallop while i <= len(temp_array) - 1 and j <= b[1]: # if elem in a is smaller, a wins if temp_array[i] <= lst[j]: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k += 1 i += 1 a_count += 1 b_count = 0 # If a runs out during linear merge # Copy the rest of b if i > len(temp_array) - 1: while j <= b[1]: lst[k] = lst[j] k += 1 j += 1 return # threshold reached, switch to gallop if a_count >= gallop_thresh: break # if elem in b is smaller, b wins else: lst[k] = lst[j] k += 1 j += 1 a_count = 0 b_count += 1 # If b runs out during linear merge # copy the rest of a if j > b[1]: while i <= len(temp_array) - 1: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k += 1 i += 1 return # threshold reached, switch to gallop if b_count >= gallop_thresh: break # If one run is winning consistently, switch to galloping mode. # i, j, and k are incremented accordingly while True: # Look for the position of b[j] in a # bisect_left() -> a_adv = index in the slice [i: len(temp_array)] # so that every elem before temp_array[a_adv] is strictly smaller than lst[j] a_adv = gallop(temp_array, lst[j], i, len(temp_array), True) # Copy the elements prior to a_adv to the merge area, increment k for x in range(i, a_adv): lst[k] = temp_array[x] k += 1 # Update the a_count to check successfulness of galloping a_count = a_adv - i # Advance i to a_adv i = a_adv # If run a runs out if i > len(temp_array) - 1: # Copy all of b over, if there is any left while j <= b[1]: lst[k] = lst[j] k += 1 j += 1 return # Copy b[j] over lst[k] = lst[j] k += 1 j += 1 # If b runs out if j > b[1]: # Copy all of a over, if there is any left while i < len(temp_array): lst[k] = temp_array[i] k += 1 i += 1 return # ------------------------------------------------------ # Look for the position of a[i] in b # b_adv is analogous to a_adv b_adv = gallop(lst, temp_array[i], j, b[1] + 1, True) for y in range(j, b_adv): lst[k] = lst[y] k += 1 # Update the counters and check the conditions b_count = b_adv - j j = b_adv # If b runs out if j > b[1]: # copy the rest of a over while i <= len(temp_array) - 1: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k += 1 i += 1 return # copy a[i] over to the merge area lst[k] = temp_array[i] i += 1 k += 1 # If a runs out if i > len(temp_array) - 1: # copy the rest of b over while j <= b[1]: lst[k] = lst[j] k += 1 j += 1 return # if galloping proves to be unsuccessful, return to linear if a_count < gallop_thresh and b_count < gallop_thresh: break # punishment for leaving galloping # makes it harder to enter galloping next time gallop_thresh += 1 def merge_high(lst, a, b, min_gallop): """Merges the two runs quasi in-place if b is the smaller run - Analogous to merge_low, but starts from the end - a and b are lists that store data of runs - min_gallop: threshold needed to switch to galloping mode - galloping mode: uses gallop() to 'skip' elements instead of linear merge""" # Make a copy of b, the smaller run temp_array = make_temp_array(lst, b[0], b[1]) # Counter for the merge area, starts at the last index of array b k = b[1] # Counter for the temp array i = len(temp_array) - 1 # Lower bound is 0 # Counter for a, starts at the end this time j = a[1] gallop_thresh = min_gallop while True: a_count = 0 # number of times a win in a row b_count = 0 # number of times b win in a row # Linear merge, taking note of how many times a and b wins in a row. # If a_count or b_count > threshold, switch to gallop while i >= 0 and j >= a[0]: if temp_array[i] > lst[j]: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k -= 1 i -= 1 a_count = 0 b_count += 1 # If b runs out during linear merge if i < 0: while j >= a[0]: lst[k] = lst[j] k -= 1 j -= 1 return if b_count >= gallop_thresh: break else: lst[k] = lst[j] k -= 1 j -= 1 a_count += 1 b_count = 0 # If a runs out during linear merge if j < a[0]: while i >= 0: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k -= 1 i -= 1 return if a_count >= gallop_thresh: break # i, j, k are DECREMENTED in this case while True: # Look for the position of b[i] in a[0, j + 1] # ltr = False -> uses bisect_right() a_adv = gallop(lst, temp_array[i], a[0], j + 1, False) # Copy the elements from a_adv -> j to merge area # Go backwards to the index a_adv for x in range(j, a_adv - 1, -1): lst[k] = lst[x] k -= 1 # # Update the a_count to check successfulness of galloping a_count = j - a_adv + 1 # Decrement index j j = a_adv - 1 # If run a runs out: if j < a[0]: while i >= 0: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k -= 1 i -= 1 return # Copy the b[i] into the merge area lst[k] = temp_array[i] k -= 1 i -= 1 # If a runs out: if i < 0: while j >= a[0]: lst[k] = lst[j] k -= 1 j -= 1 return # ------------------------------------------------- # Look for the position of A[j] in B: b_adv = gallop(temp_array, lst[j], 0, i + 1, False) for y in range(i, b_adv - 1, -1): lst[k] = temp_array[y] k -= 1 b_count = i - b_adv + 1 i = b_adv - 1 # If b runs out: if i < 0: while j >= a[0]: lst[k] = lst[j] k -= 1 j -= 1 return # Copy the a[j] back to the merge area lst[k] = lst[j] k -= 1 j -= 1 # If a runs out: if j < a[0]: while i >= 0: lst[k] = temp_array[i] k -= 1 i -= 1 return # if galloping proves to be unsuccessful, return to linear if a_count < gallop_thresh and b_count < gallop_thresh: break # punishment for leaving galloping gallop_thresh += 1 def merge_collapse(lst, stack): """The last three runs in the stack is A, B, C. Maintains invariants so that their lengths: A > B + C, B > C Translated to stack positions: stack[-3] > stack[-2] + stack[-1] stack[-2] > stack[-1] Takes a stack that holds many lists of type [s, e, bool, length]""" # This loops keeps running until stack has one element # or the invariant holds. while len(stack) > 1: if len(stack) >= 3 and stack[-3][3] <= stack[-2][3] + stack[-1][3]: if stack[-3][3] < stack[-1][3]: # merge -3 and -2, merge at -3 merge(lst, stack, -3) else: # merge -2 and -1, merge at -2 merge(lst, stack, -2) elif stack[-2][3] <= stack[-1][3]: # merge -2 and -1, merge at -2 merge(lst, stack, -2) else: break def merge_force_collapse(lst, stack): """When the invariant holds and there are > 1 run in the stack, this function finishes the merging""" while len(stack) > 1: # Only merges at -2, because when the invariant holds, # merging would be balanced merge(lst, stack, -2) # Starting index s = 0 # Ending index e = len(lst) - 1 # The stack stack = [] # Compute min_run using size of lst min_run = merge_compute_minrun(len(lst)) while s <= e: # Find a run, return [start, end, bool, length] run = count_run(lst, s) # If decreasing, reverse if run[2] == False: reverse(lst, run[0], run[1]) # Change bool to True run[2] = True # If length of the run is less than min_run if run[3] < min_run: # The number of indices by which we want to extend the run # either by the distance to the end of the lst # or by the length difference between run and minrun extend = min(min_run - run[3], e - run[1]) # Extend the run using binary insertion sort bin_sort(lst, run[0], run[1], extend) # Update last index of the run run[1] = run[1] + extend # Update the run length run[3] = run[3] + extend # Push the run into the stack stack.append(run) # Start merging to maintain the invariant merge_collapse(lst, stack) # Update starting position to find the next run # If run[1] == end of the lst, s > e, loop exits s = run[1] + 1 # Some runs might be left in the stack, complete the merging. merge_force_collapse(lst, stack) return lst속도 테스트
1. 크기 100
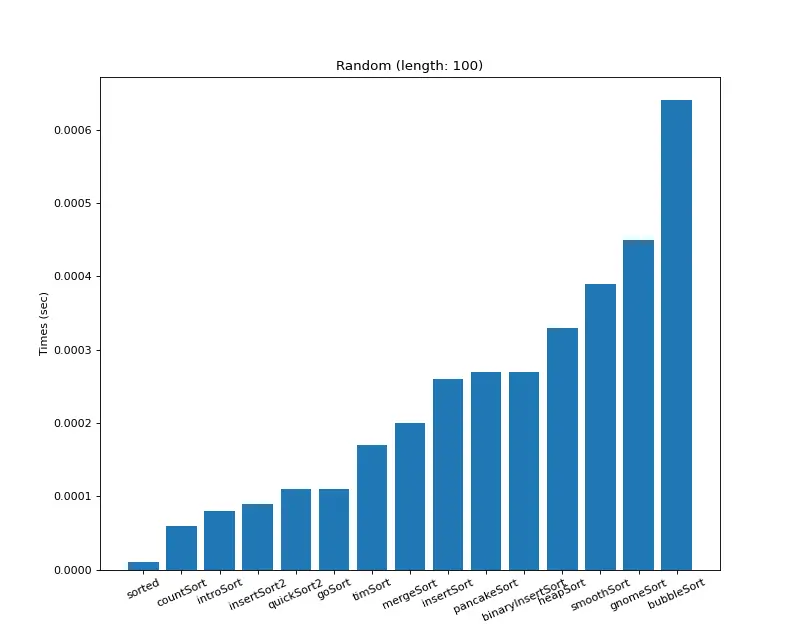
크기 100 (랜덤) 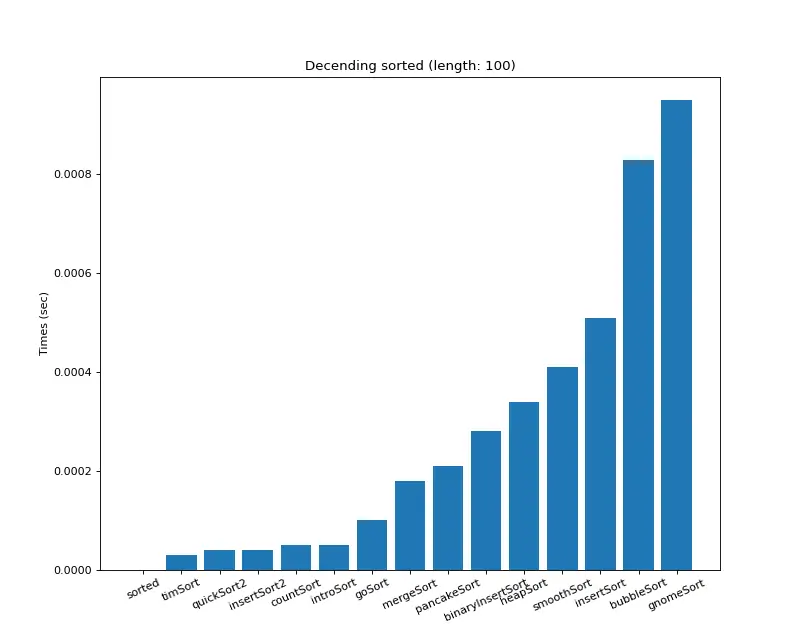
크기 100 (내림차순 배열) 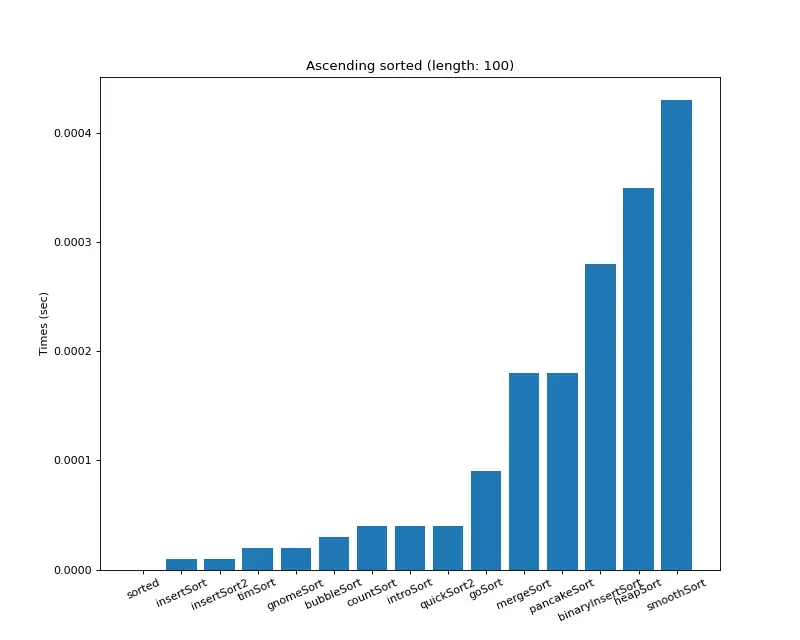
크기 100 (오름차순 배열) 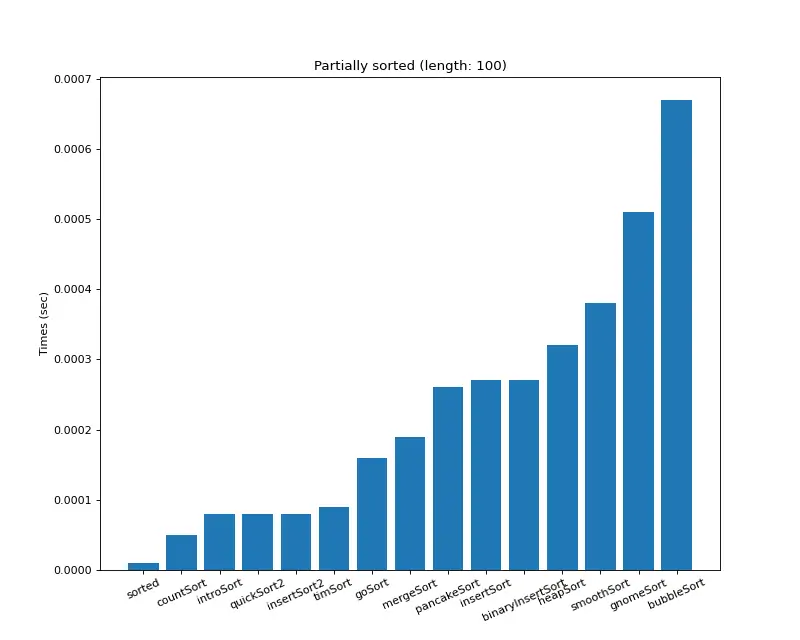
크기 100 (부분 정렬) 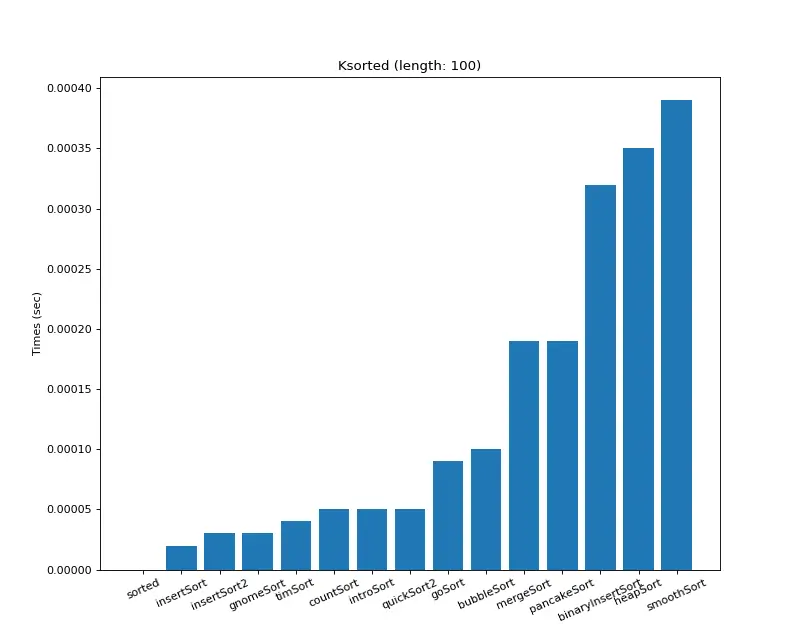
크기 100 (K정렬) 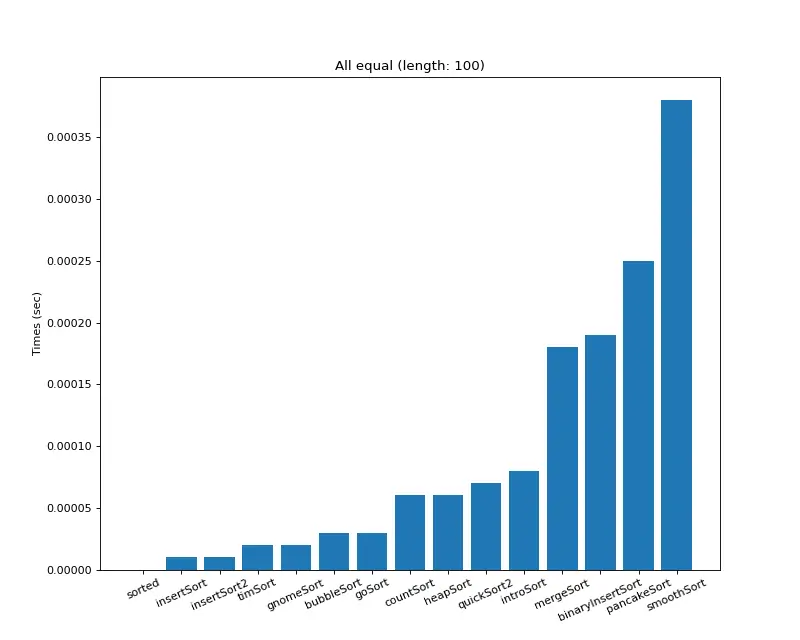
크기 100 (모두 같은 값) 
크기 100 (거의 모두 같은 값) 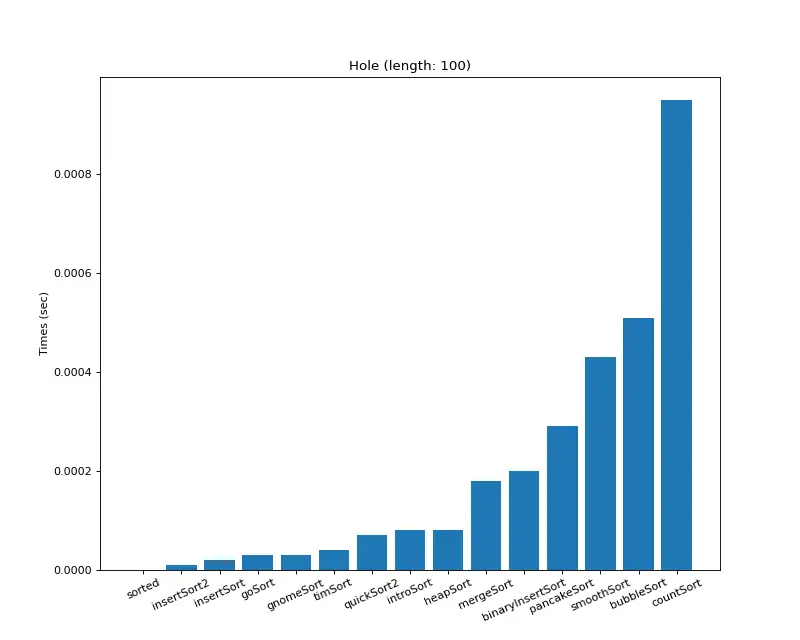
크기 100 (하나만 다른 값) 2. 크기 10,000
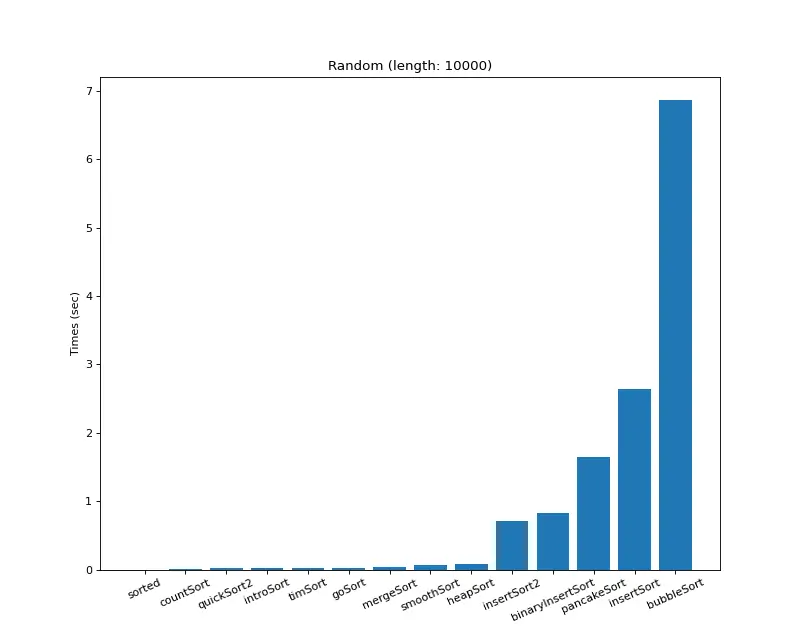
크기 10,000 (랜덤) 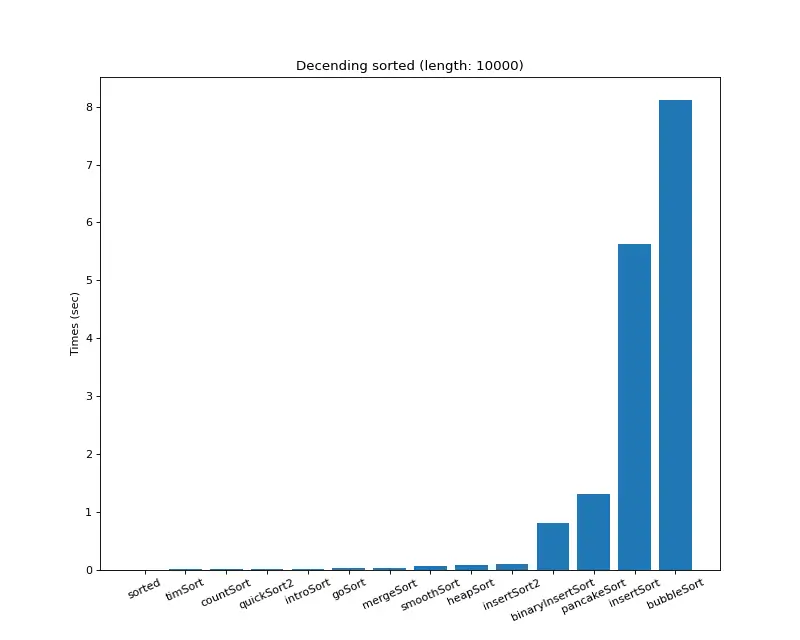
크기 10,000 (내림차순 배열) 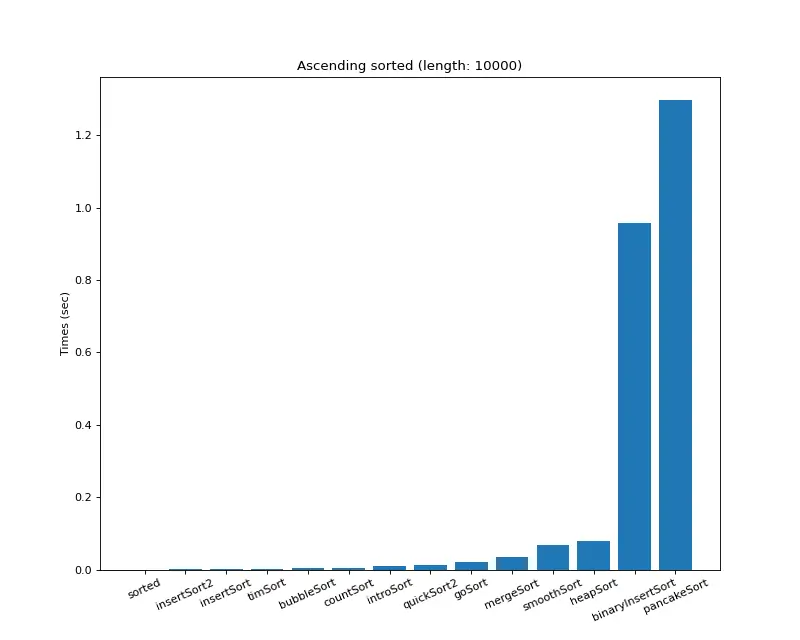
크기 10,000 (오름차순 배열) 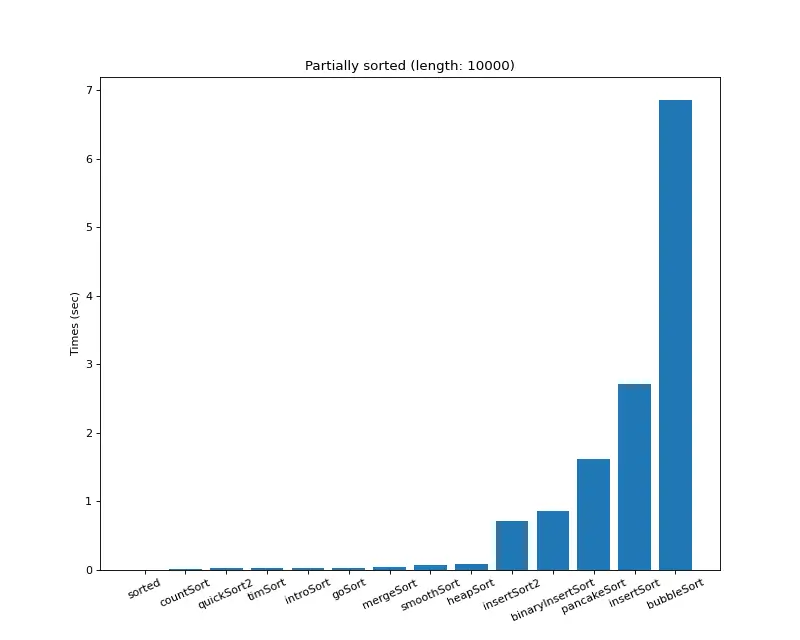
크기 10,000 (부분 정렬) 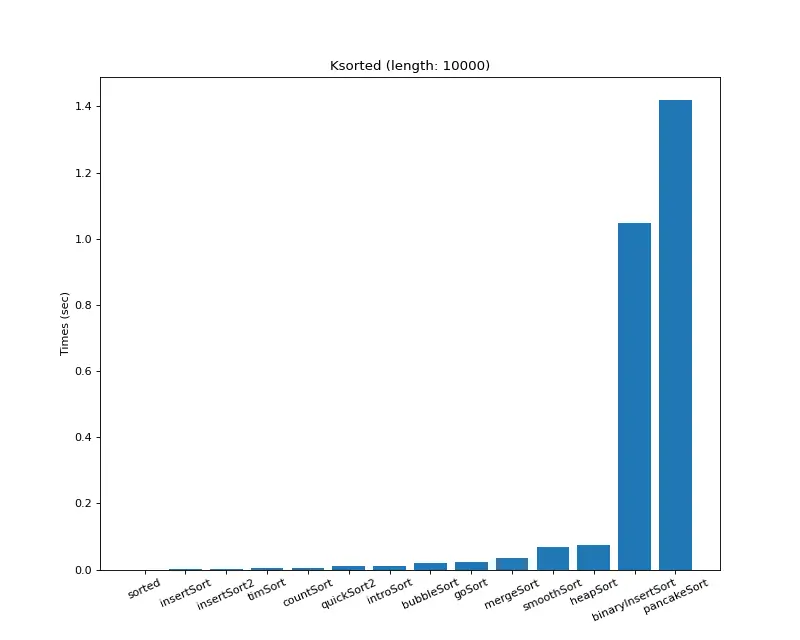
크기 10,000 (K정렬) 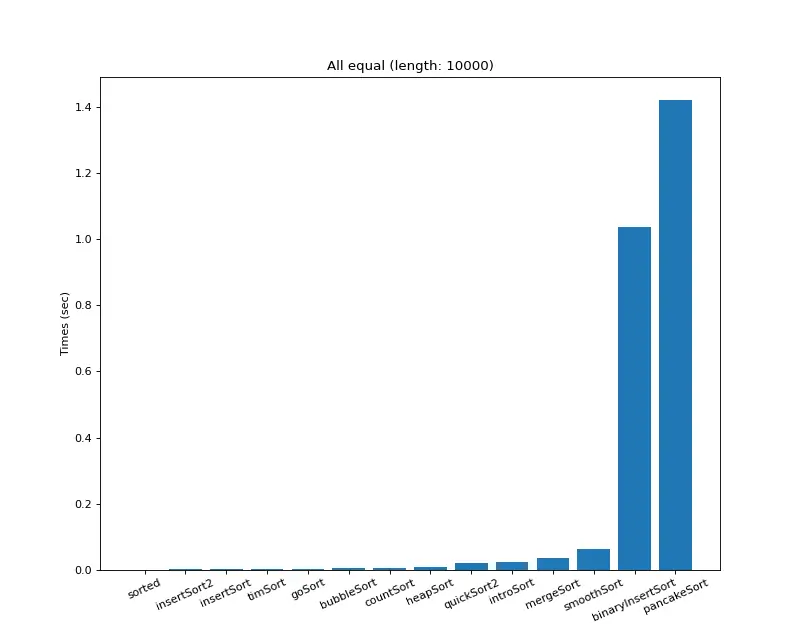
크기 10,000 (모두 같은 값) 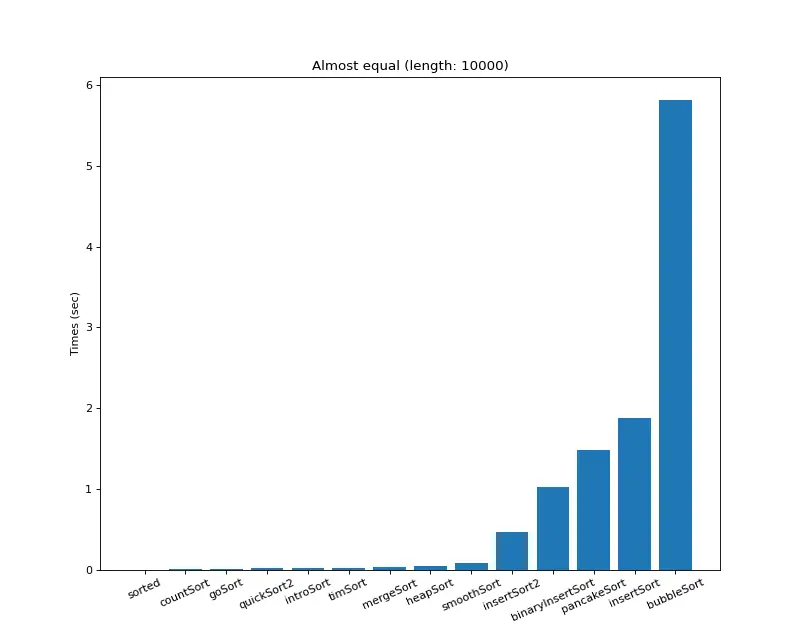
크기 10,000 (거의 모두 같은 값) 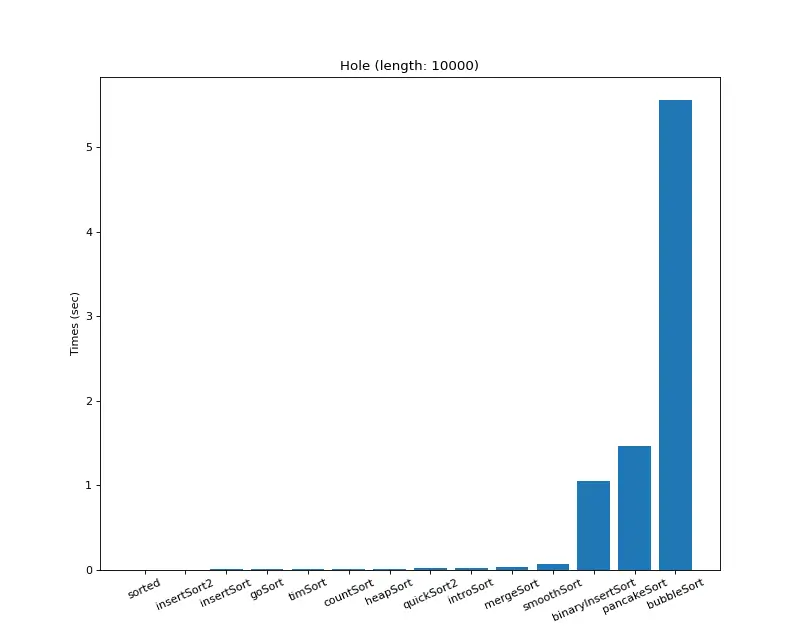
크기 10,000 (하나만 다른 값) 3. 크기 1,000,000 (백만)

크기 백만 (랜덤) 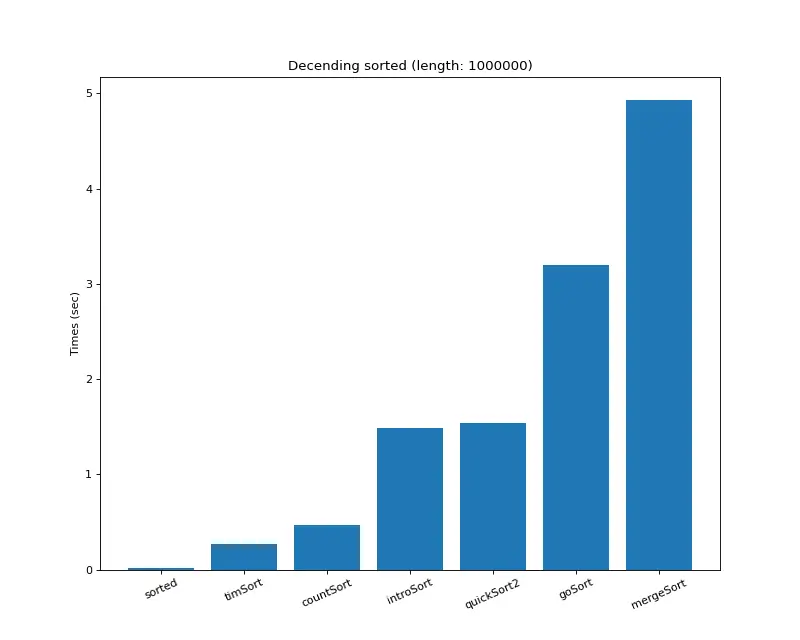
크기 백만 (내림차순 배열) 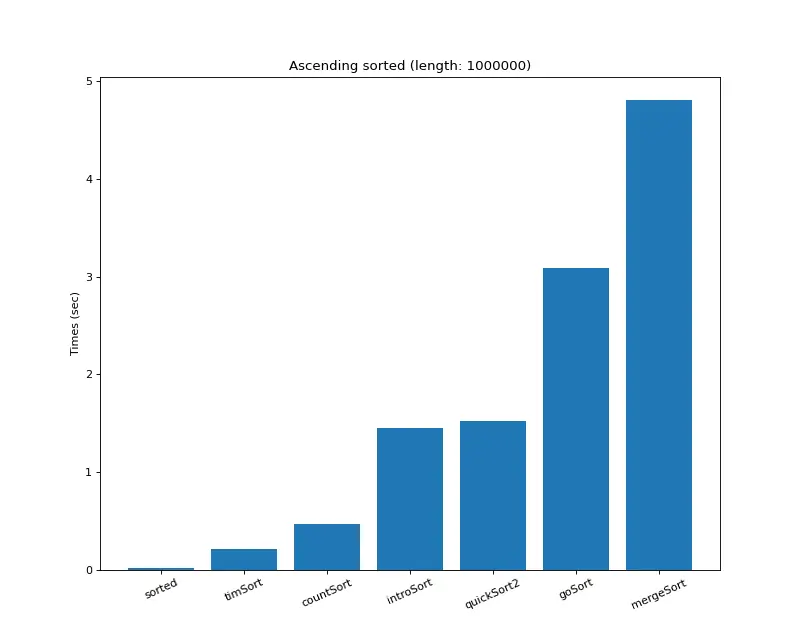
크기 백만 (오름차순 배열) 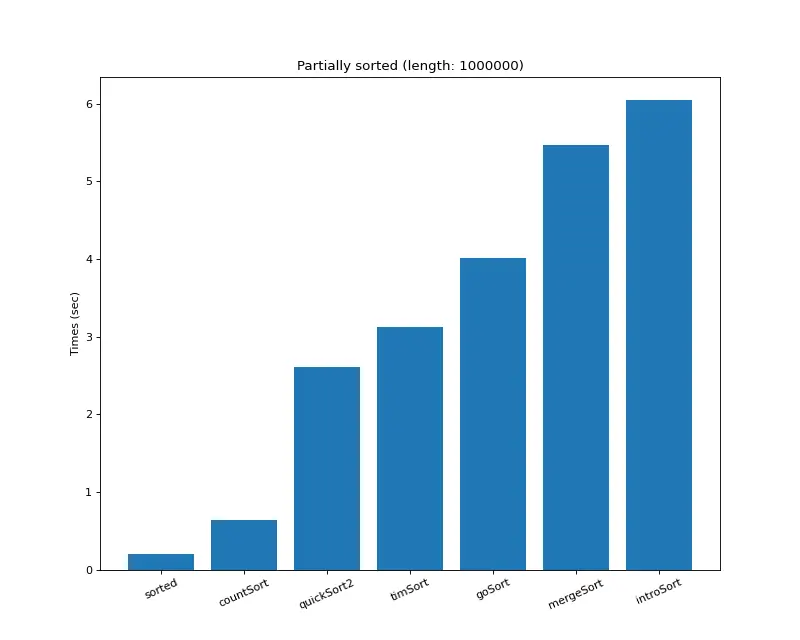
크기 백만 (부분 정렬) 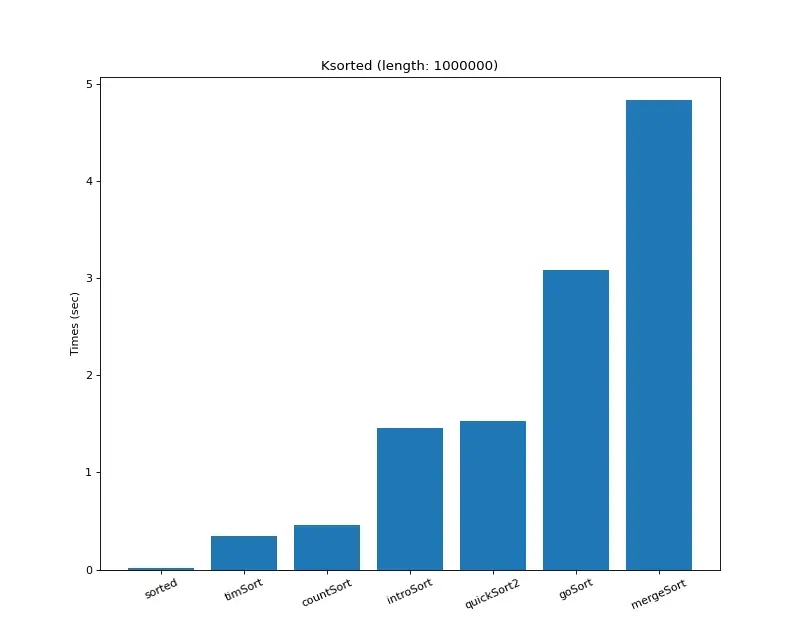
크기 백만 (k정렬) 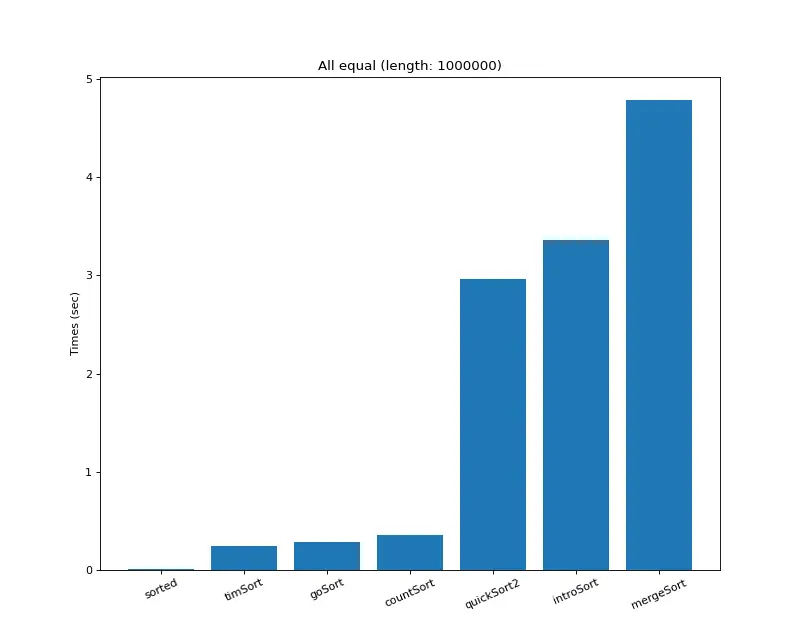
크기 백만 (다 같은 값) 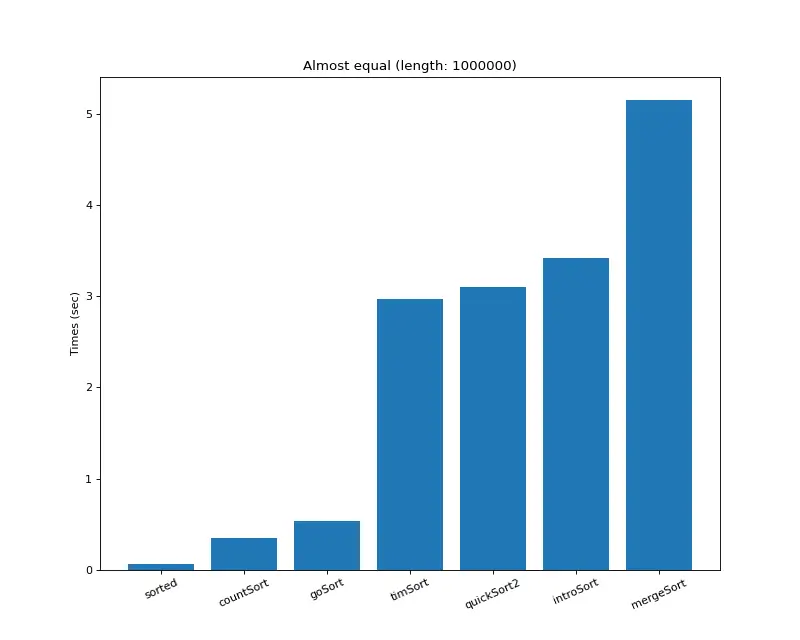
크기 백만 (거의 모두 같은 값) 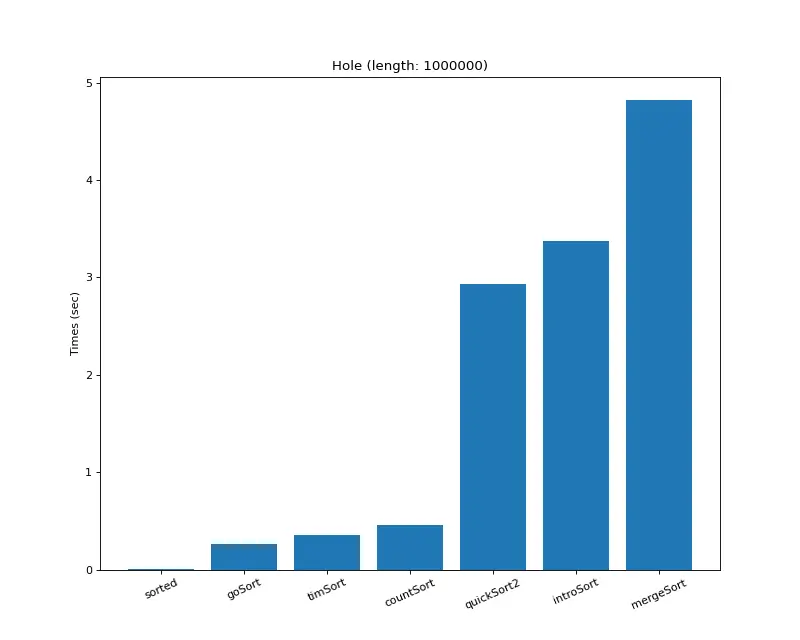
크기 백만 (하나만 다른 값) 배열 생성기 및 시간 복잡도 계산기 : choiseokwon.tistory.com/231
파이썬 정렬 알고리즘 big-O 시간 복잡도 계산하기
big-O Caculator v0.0.9.5 big-O-calculator A calculator to predict big-O of sorting functions pypi.org 1. 소개 C++ 버전에서 아이디어를 얻어 파이썬으로 모듈화 시키고 pypi에 업로드 해보았다. 시간 복..
choiseokwon.tistory.com
풀 코드 확인하기 : https://gist.github.com/Alfex4936/e8b6b7c06a181d3faa84b155b20e6de6
TimSort + Introspective Sort + bogo Sort + pancake Sort + Insertion Sort + Binary Insertion Sort + Count Sort + Merge Sort + Qui
TimSort + Introspective Sort + bogo Sort + pancake Sort + Insertion Sort + Binary Insertion Sort + Count Sort + Merge Sort + Quick Sort + Bubble Sort - Python Sorting Algorithms.py
gist.github.com
※ 부정확한 코드들도 있음
728x90'컴퓨터 > 파이썬' 카테고리의 다른 글
Python Microsoft Playwright (0) 2020.08.16 파이썬 OpenCV 이미지 차이 구하기 (2) 2020.08.06 파이썬 Smooth Sort (부드러운 정렬 알고리즘) (0) 2020.08.03