-
파이썬 Smooth Sort (부드러운 정렬 알고리즘)컴퓨터/파이썬 2020. 8. 3. 13:12728x90반응형
Smooth Sort
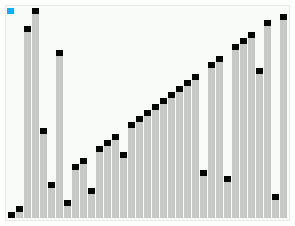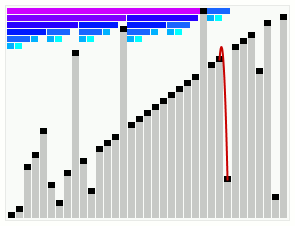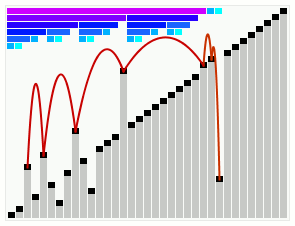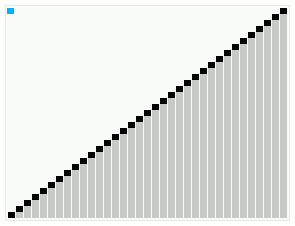
@wikipedia 소개 : 부드러운 정렬은 길 찾기로 유명한 데이크스트라분이 1981년에 발표한 정렬 알고리즘이다.
HeapSort의 변형 중 하나이며, in-place, not stable
시간 복잡도는 최고 : O($n$) = (대부분 정렬된 상태일 경우)
평균 : O($nlogn$), 최악 : O($nlogn$) 공간 복잡도는 총 O($n$), 보조(O($1$))
특이한 점은 Leonardo number라는 수학 개념을 Heap Sort에 적용시킨 점이다.
1. Leonardo Number
피보나치 수열과 비슷한데, 다음과 같이 진행된다.
$1, 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 25, 41, 67, 109, 177, 287, 465, 753, 1219, 1973, 3193, 5167, 8361 ...$
실제로 아래 수식을 적용하면 피보나치 수열로 바꿀 수 있다.
$L(n) = 2F(n + 1) - 1, n >= 0$
그럼 이 Leonardo Number를 어떻게 정렬 알고리즘에 사용했을까? 일단 파이썬 코드를 보겠다.
def numbersLeonardo(size): numbers = [1, 1] nextNumber = numbers[-1] + numbers[-2] + 1 while len(numbers) >= 2 and size > nextNumber: numbers.append(nextNumber) nextNumber = numbers[-1] + numbers[-2] + 1 numbers.reverse() return numbers def arrToHeap(data): # 배열을 받으면 heap 구조로 바꿈 leonardoNumbers = numbersLeonardo(len(data)) listHeaps = [] m = 0 for i in leonardoNumbers: # 아직 할당 안된 배열이 다음 레오나르도 수보다 크거나 같으면 if len(data) - m >= i: listHeaps.append(data[m: m+i]) # 할당 안된 부분으로 이동 m += i # 힙 성질 맞추기 for i in listHeaps: heapq.heapify(i) # heap은 non-decreasing이기 때문에 뒤집기 listHeaps.reverse() return listHeaps자식 노드는 절대 부모보다 큰 값을 가질 수 없고 (둘 다 1일 땐 예외)
자식들의 크기는 레오나르도 수열을 따라서, 힙은 아래처럼 생성된다.
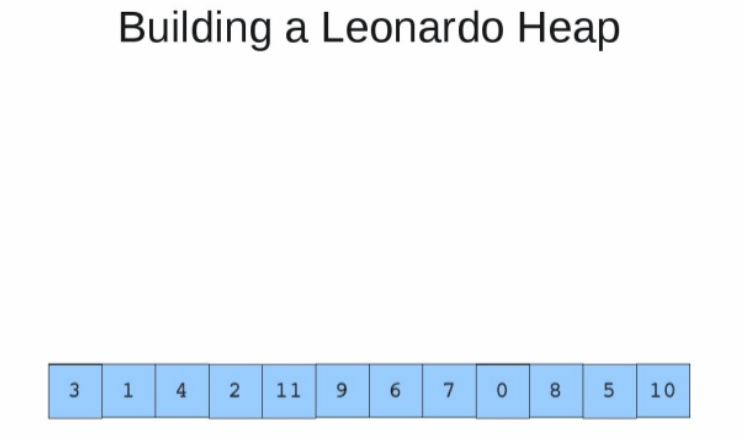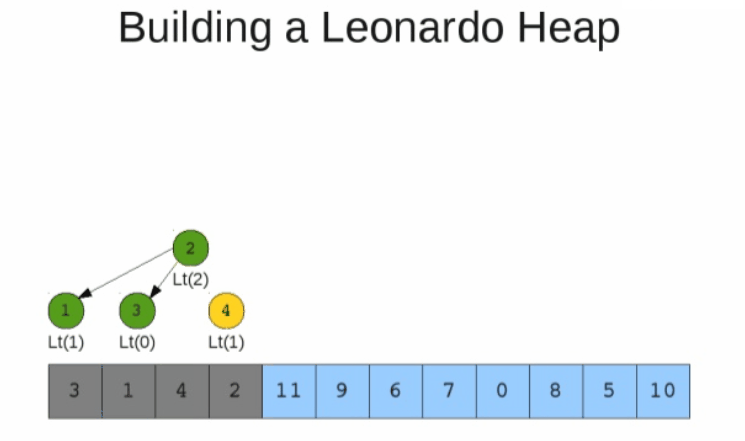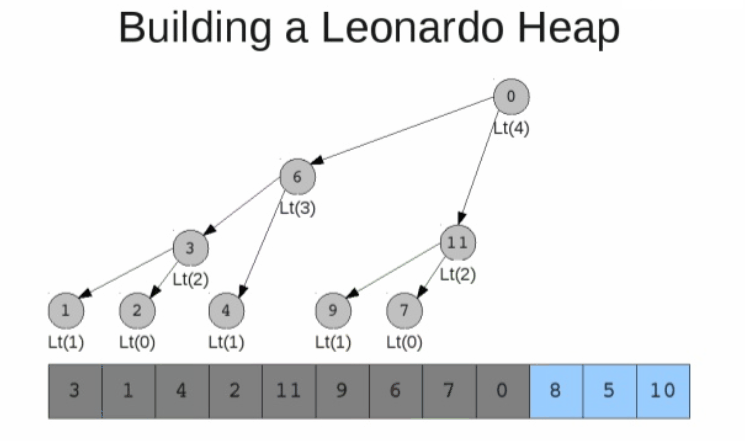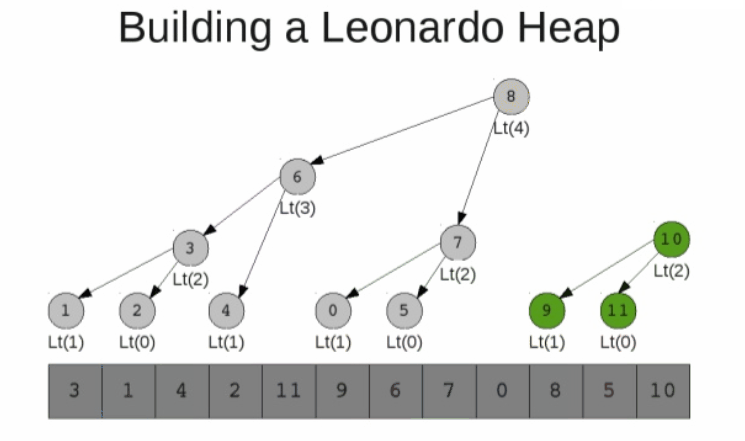

Dijikstra : 누군가는 제가 왜 stretch 길이에 레오나르도 수를 사용했는지 물을 수 있습니다,
... 63 31 15 7 3 1, 이 수들은 곧 확률이고,
Completely Balanced 트리에서 각 stretch는 후위 순회(post-order) 결과처럼 보였습니다.
저는 제가 왜 레오나르도 수를 선택했는지 잘 알고 있습니다, Balanced 트리에서 stretch 평균 수는 레오나르도 수들에
$1.2559$ ( = $(1/4) · (5+sqrt(5)) · (log2(1+sqrt(5))-1$) 배를 한 것과 같았기 때문이죠.
음...말이 어렵다stretch = 각 노드를 이 노드보다 값이 작은 K 개의 노드들로 바꾸는 것
ex) 아래 트리에 stretch(3)을 하면, root(12)는 값 4의 노드 3개를 갖고, node(81)은 값 34의 노드 3개로 stretch
root = Node(12) root.left = Node(81) root.left.right = Node(56)2. Smooth Sort 구현하기
사실 Leonardo 수를 이용한 것 빼고는 별 것 없다.
Heap Sort에 Leonardo 수를 이용해 heap만 만들면 되기 때문이다.
(Heaps들이 완전한 Balanced 상태는 아니다, 그래서 remark3, 힙 크기를 N^2 - 1로 하면 balanced가 됨)
import heapq def numbersLeonardo(size): numbers = [1, 1] nextNumber = numbers[-1] + numbers[-2] + 1 while len(numbers) >= 2 and size > nextNumber: numbers.append(nextNumber) nextNumber = numbers[-1] + numbers[-2] + 1 numbers.reverse() return numbers def arrToHeap(data): # 배열을 받으면 heap 구조로 바꿈 leonardoNumbers = numbersLeonardo(len(data)) listHeaps = [] m = 0 for i in leonardoNumbers: # 아직 할당 안된 배열이 다음 레오나르도 수보다 크거나 같으면 if len(data) - m >= i: listHeaps.append(data[m: m+i]) # 할당 안된 부분으로 이동 m += i # 힙 성질 맞추기 for i in listHeaps: heapq.heapify(i) # heap은 non-decreasing이기 때문에 뒤집기 listHeaps.reverse() return listHeaps def countIndexes(i, indexes): indexes.append(2*indexes[i]+1) indexes.append(2*indexes[i]+2) return indexes def getList(indexPart, heap): heapPart = [] for i in indexPart: if i < len(heap): heapPart.append(heap[i]) return heapPart def heapDivision(heap): heapleft = [] heapright = [] index = 0 indexesLeft = [1] indexesRight = [2] while indexesLeft[-1] < len(heap): indexesLeft = countIndexes(index, indexesLeft) indexesRight = countIndexes(index, indexesRight) index += 1 heapleft = getList(indexesLeft, heap) heapright = getList(indexesRight, heap) return heapleft, heapright # Time Complexity O(n) | O(nlogn) | O(nlogn) # Space Complexity AUX : O(1), Total : O(n) def smoothSort(array): listHeaps = arrToHeap(array) result = [] heapLeft, heapRight = 0, 0 while (listHeaps): flag = 0 minIndex = listHeaps.index(min(listHeaps)) currentRoot = listHeaps[0][0] currentMin = listHeaps[minIndex][0] heapq.heapreplace(listHeaps[0], currentMin) heapq.heapreplace(listHeaps[minIndex], currentRoot) if len(listHeaps[0]) > 1: heapLeft, heapRight = heapDivision(listHeaps[0]) flag = 1 minimum = heapq.heappop(listHeaps[0]) result.append(minimum) listHeaps.pop(0) if flag == 1: listHeaps.insert(0, heapLeft) listHeaps.insert(0, heapRight) return result3. 얼마나 빠른가?
테스트 배열을 3번 실행해서, 가장 빠르게 정렬된 시간을 출력하도록 했다.
1. 랜덤한 숫자 5000개
array = [randint(-5000, 5000) for i in range(5000)]# 결과 def: sorted(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00100초 def: countSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00300초 def: introSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01400초 def: quickSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01800초 def: mergeSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.02400초 def: smoothSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03200초 def: timSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03500초 def: heapSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03500초 def: insertSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 1.59100초 def: bubbleSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 2.55200초1위 : arr.sorted(), 2위 : countSort(), 3위 : introSort()
4위 : quickSort(), 5위: mergeSort(), 6위: smoothSort()
7위 : timSort(), 8위: heapSort(), 9위 : insertSort(), 10위: bubbleSort()
2. 거꾸로 정렬된 크기 5000의 배열 (Descending)
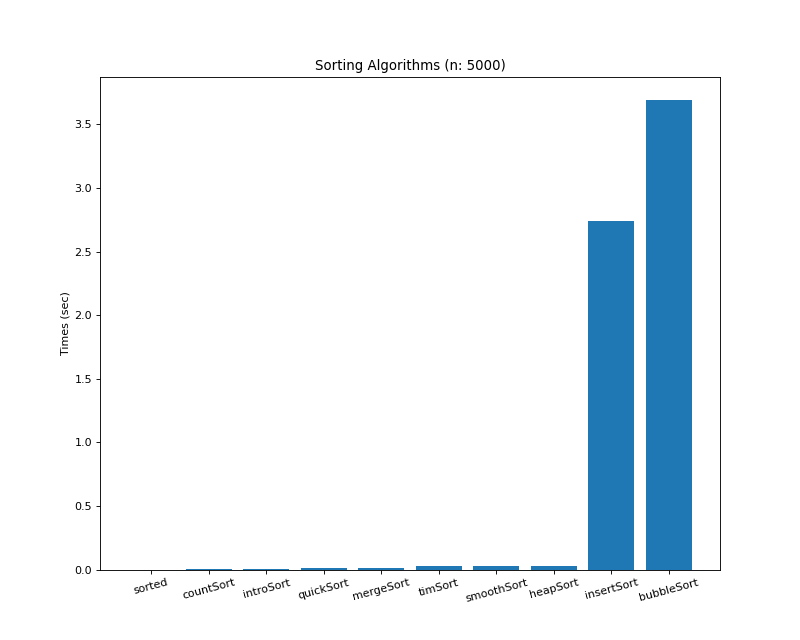
array = [i for i in reversed(range(5000))]# 결과 def: sorted(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00000초 def: countSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00200초 def: introSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00600초 def: quickSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01400초 def: mergeSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01500초 def: timSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.02600초 def: smoothSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.02800초 def: heapSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.02900초 def: insertSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 2.73700초 def: bubbleSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 3.69000초1위 : arr.sorted(), 2위 : countSort(), 3위 : introSort()
4위 : quickSort(), 5위: mergeSort(), 6위: timSort()
7위 : smoothSort(), 8위: heapSort(), 9위 : insertSort(), 10위: bubbleSort()
3. 정렬된 크기 5000 배열 (Ascending)
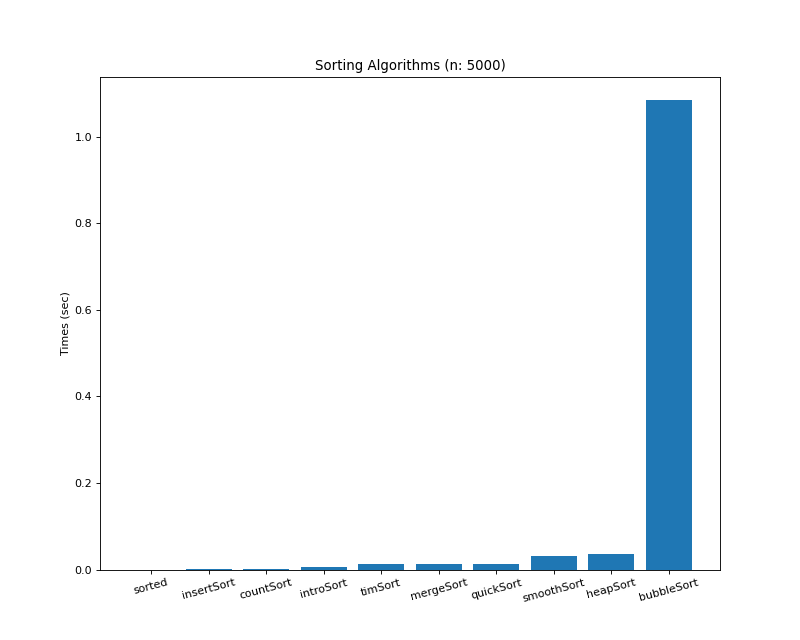
array = [i for i in range(5000)]# 결과 def: sorted(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00000초 def: insertSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00100초 def: countSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00200초 def: introSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00600초 def: timSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01300초 def: mergeSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01300초 def: quickSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01400초 def: smoothSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03100초 def: heapSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03600초 def: bubbleSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 1.08400초1위 : arr.sorted(), 2위 : insertSort(), 3위 : countSort()
4위 : introSort(), 5위: timSort(), 6위: mergeSort()
7위 : quickSort(), 8위: smoothSort(), 9위 : heapSort(), 10위: bubbleSort()
4. 크기 5000의 부분 정렬된 랜덤 배열
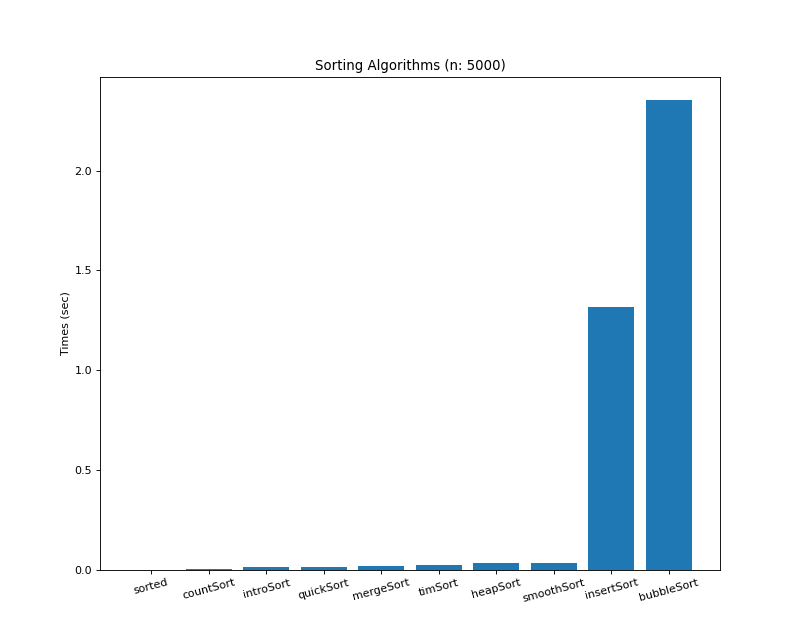
array4 = [randint(-5000, 5000) for i in range(5000//3)] + \ [i for i in range(5000//3)] + \ [1] + \ [i for i in reversed(range(5000//3))]# 결과 def: sorted(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00000초 def: countSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.00300초 def: introSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01200초 def: quickSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01300초 def: mergeSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.01800초 def: timSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.02100초 def: heapSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03100초 def: smoothSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 0.03100초 def: insertSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 1.31700초 def: bubbleSort(), 최소 실행 시간: 2.35200초1위 : arr.sorted(), 2위 : countSort(), 3위 : introSort()
4위 : quickSort(), 5위: mergeSort(), 6위: timSort()
7위 : heapSort(), 8위: smoothSort(), 9위 : insertSort(), 10위: bubbleSort()
참고 : https://github.com/jasondavies/smoothsort.js/blob/master/smoothsort.js
참고 : https://code.google.com/archive/p/combsortcs2p-and-other-sorting-algorithms/wikis/SmoothSort.wiki
참고 : http://www.cs.utexas.edu/users/EWD/transcriptions/EWD07xx/EWD796a.html
728x90'컴퓨터 > 파이썬' 카테고리의 다른 글
파이썬 OpenCV 이미지 차이 구하기 (2) 2020.08.06 파이썬 win10toast 윈도우 알림 만들기 (0) 2020.08.02 Docker + Flask 튜토리얼 (0) 2020.07.30
