-
파이썬 A* (A-star) 최단 경로 찾기 알고리즘컴퓨터/파이썬 2020. 7. 20. 16:02728x90반응형
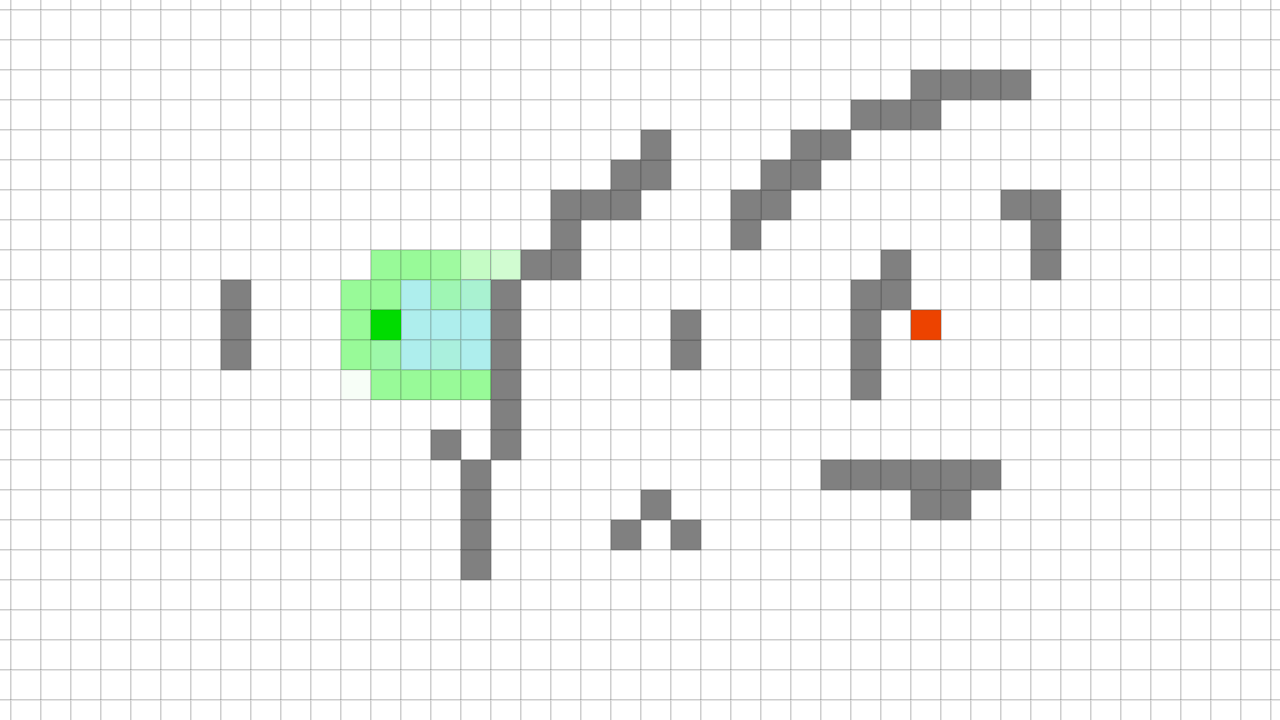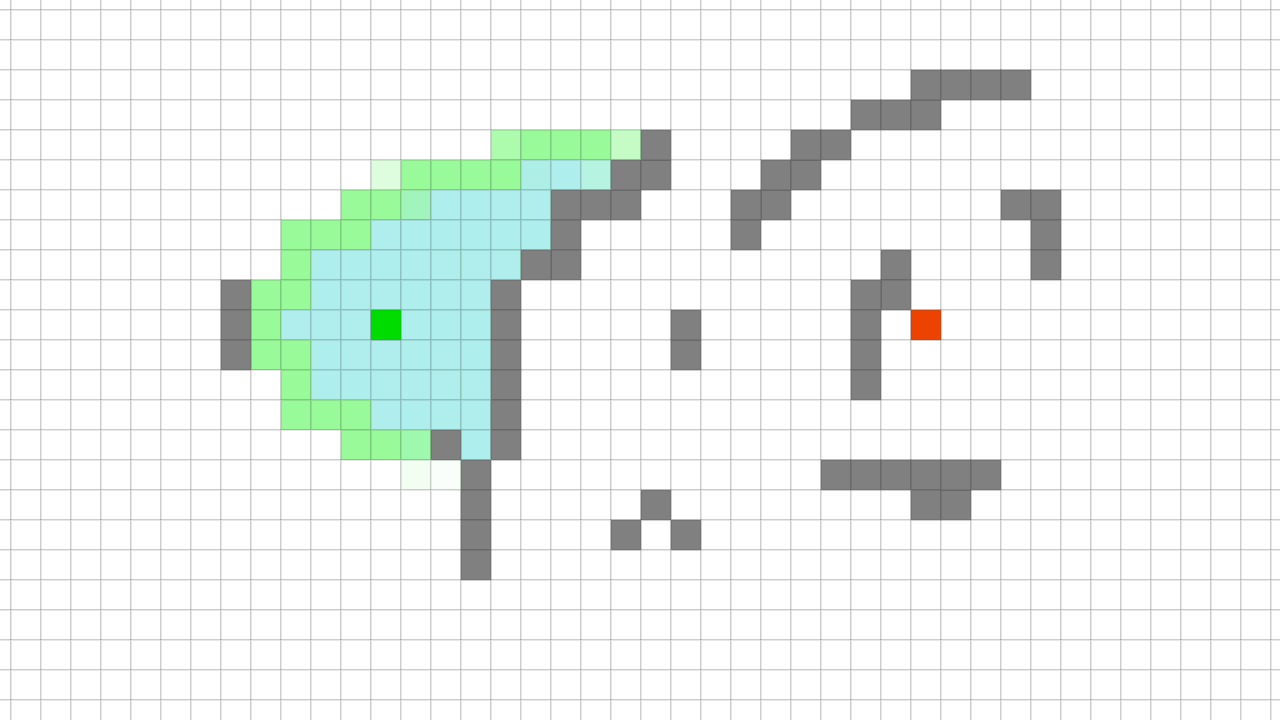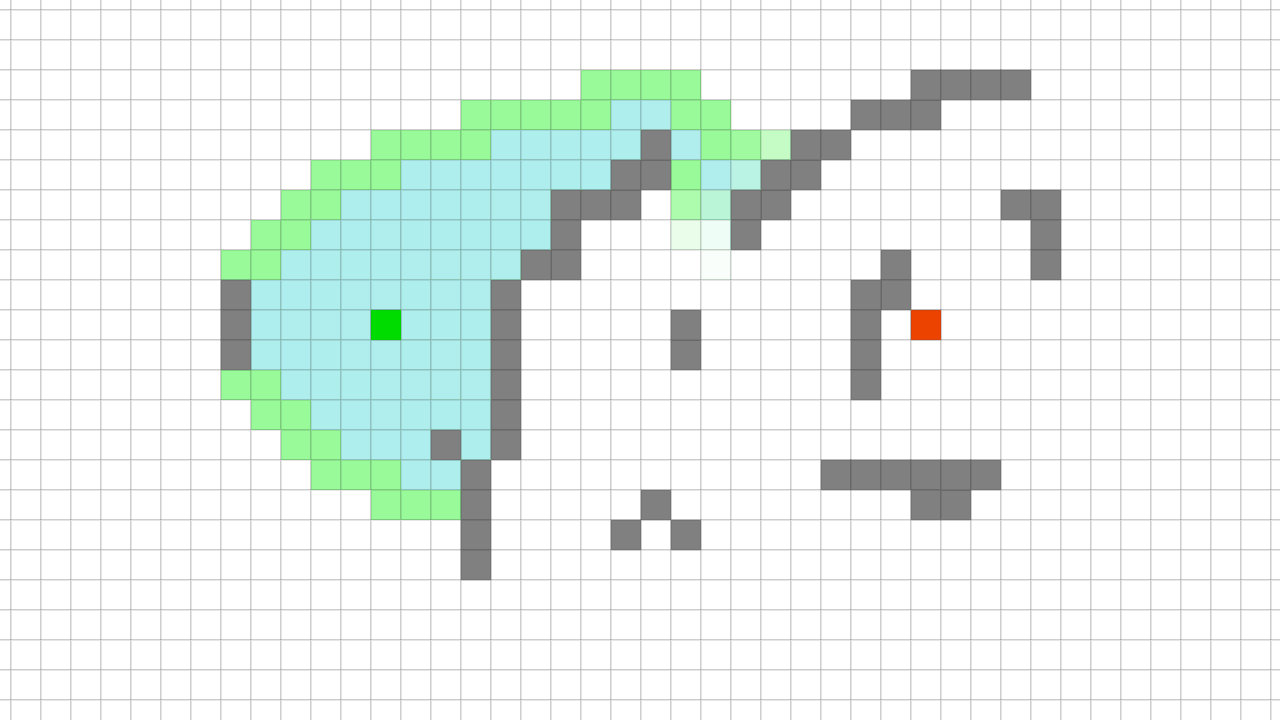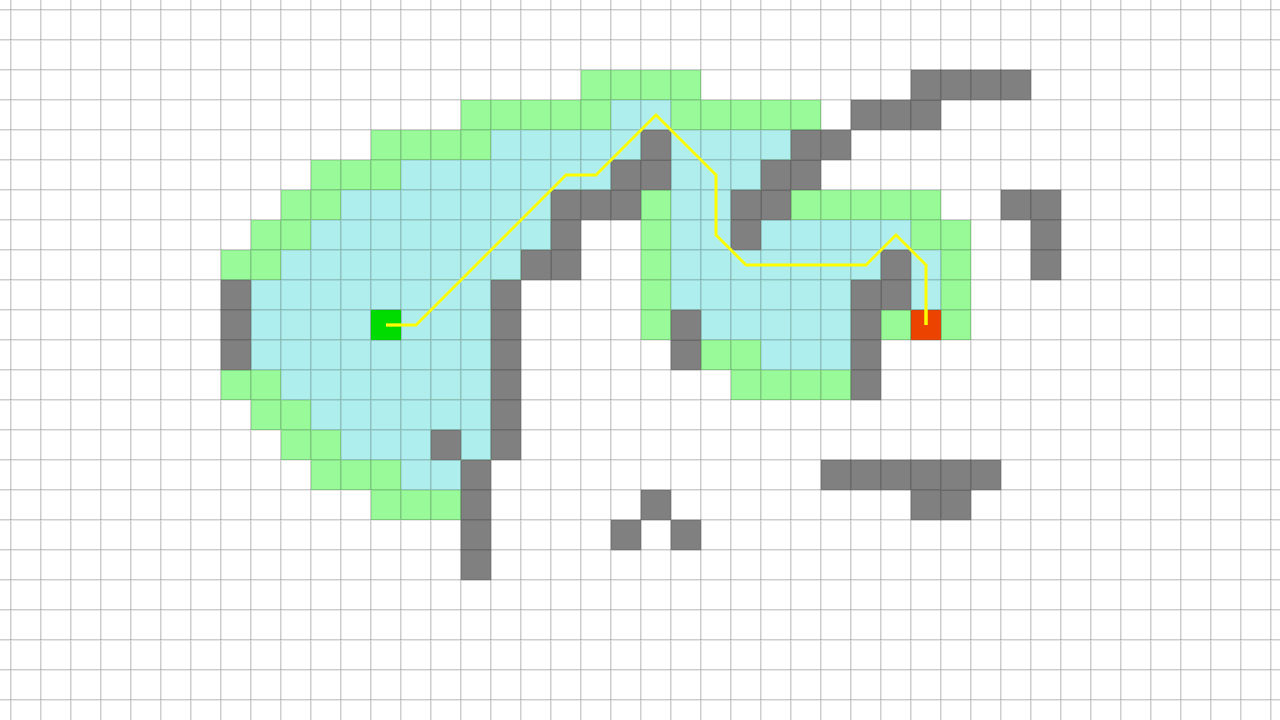
A* Pathfinding visualization A* 길 찾기 알고리즘은 1968년에 Peter Hart, Nils Nilsson, Bertram Raphael에 의해 최초 공개됐다.
우선 Node 클래스는 아래와 같이 구현될 것이며, 아래 클래스를 보고 글을 읽으면 좀 더 편할 것이다.
class Node: def __init__(self, parent=None, position=None): self.parent = parent # 이전 노드 self.position = position # 현재 위치 self.f = 0 self.g = 0 self.h = 0ex) 노드의 현재 위치는 xy좌표계를 사용한다.
start = (0, 0), end = (9,9)
aStar(star, end) -> Node(None, start)
F = G + H
우선 A* 알고리즘의 핵심 값인 F, G, H 값을 알아보겠다.
이 3개의 변수는 노드를 추가할 때마다 값이 갱신될 것이다.
- F = 출발 지점에서 목적지까지의 총 cost 합
- G = 현재 노드에서 출발 지점까지의 총 cost
- H = Heuristic(휴리스틱), 현재 노드에서 목적지까지의 추정 거리
Heuristic [휴리스틱]
형용사 (교수법·교육이) 체험적인 [스스로 발견하게 하는]f, g, h 약자는 그냥 수학에서 $f(x), g(x), h(x)$이다.이해를 돕기 위해, 아래 예제를 들어보겠다. (초록 점 = 시작, 빨간 점 = 종료)
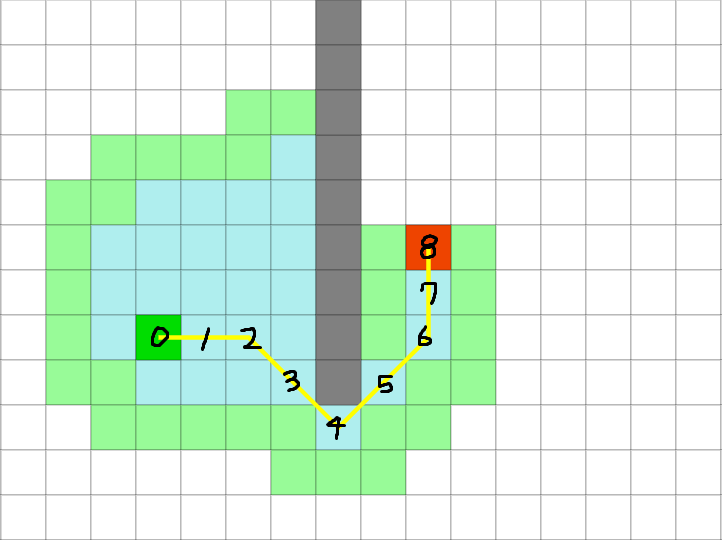
시작 노드를 node(0), 도착 노드를 node(8)
현재 노드가 node(2)라고 해보자.
G(x)
G = 현재 노드에서 출발 지점까지의 총 cost
현재 노드 = node(2), 출발 지점에서 2 cost만큼 떨어져 있다. (parent 노드는 당연히 node(1))
따라서, 현재 노드(2)는 아래와 같이 표현된다.
node(2).g = 2H(x)
H = Heuristic(휴리스틱), 현재 노드에서 목적지까지의 추정 거리
현재 노드 = node(2) 에서 목적지까지의 거리를 추정해보자. (현재 노드부터 1이라고 가정)
5 cost만큼 오른쪽→으로 가서, 위↑로 3 cost만큼 가면 목적지 노드가 있다.
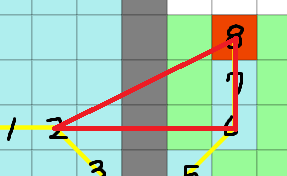
직각 삼각형의 빗변의 제곱이 두 직각변의 제곱의 합과 같다는 정리 여기서 피타고라스의 정리 $(a^2 + b^2 = c^2)$, 를 이용해서 H 값을 계산해보면,
node(2).h = $5^2 + 3^2$ = 34
$\sqrt{34}$로 지정하는 게 맞지만, 귀찮게 매번 계산 안 해도, 결과는 똑같이 나온다.하지만, 근접 거리나 값이 클 경우에는 다익지스트라처럼 작동할 수 있다.
파이썬으로는 아래와 같다. (맨해튼 거리)
child.h = ((child.position[0] - end_node.position[0]) ** 2) + \ ((child.position[1] - end_node.position[1]) ** 2)또는, 더 정확하게 하고 싶으면, octile distance + diagonal distance를 이용하면 된다.
def heuristic(node, goal, D=1, D2=2 ** 0.5): dx = abs(node.position[0] - goal.position[0]) dy = abs(node.position[1] - goal.position[1]) return D * (dx + dy) + (D2 - 2 * D) * min(dx, dy) ... child.h = heuristic(child, endNode) ...Heuristics 종류 : http://theory.stanford.edu/~amitp/GameProgramming/Heuristics.html
4방향으로 움직이면 보통, Manhatten Distance, 8방향으로 움직이면 Diagonal Distance
모든 방향은 Euclidean을 수정해서 사용하면 괜찮다. (맨해튼 거리가 제일 무난하다)
F(x)
F = 출발 지점에서 목적지까지의 총 cost 합
이제 현재 노드(node(2))의 G값과 H값을 더해보면,
node(2).f = node(2).g + node(2).h = 2 + 34 = 36
F 값 사용하기
F 값은 현재 노드가 목적지에 도달하는 데 있어서, 최선의 방법인지 확인할 수 있는 값이다.
이 F 값이 없으면, Dikjistra 길 찾기 알고리즘처럼 모든 노드에서 목적지까지 가는 방법을 찾는다.
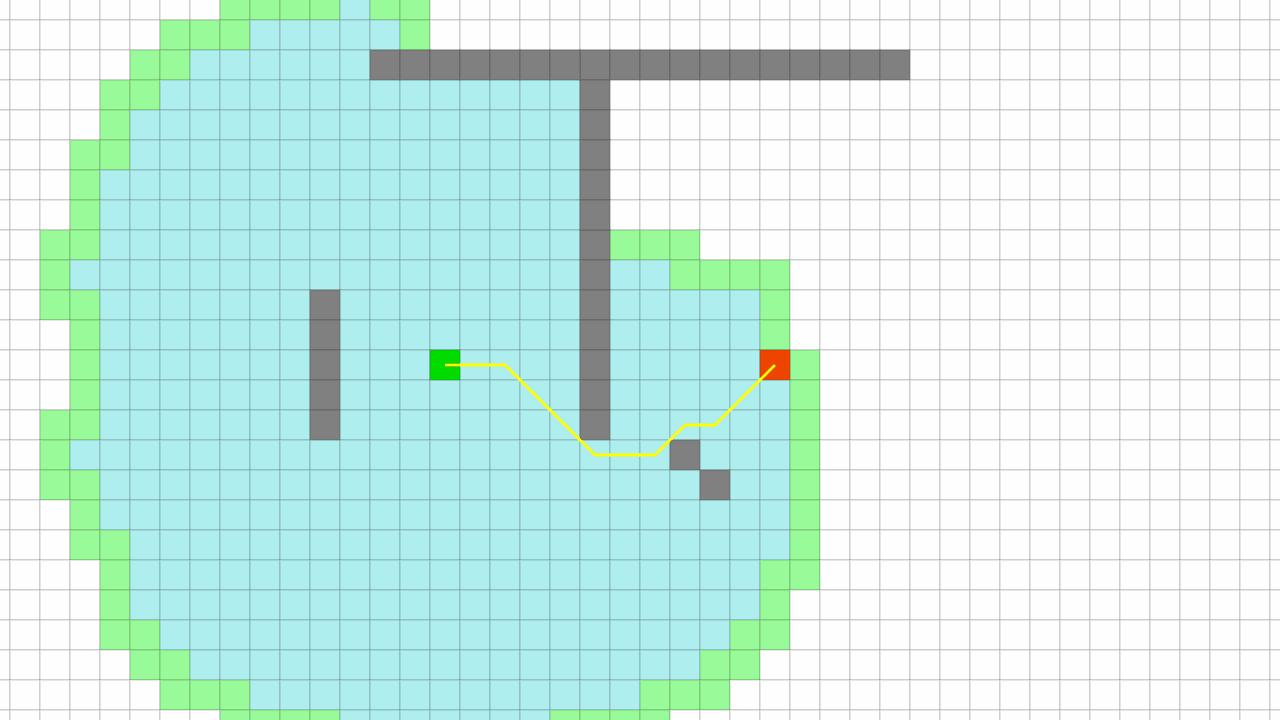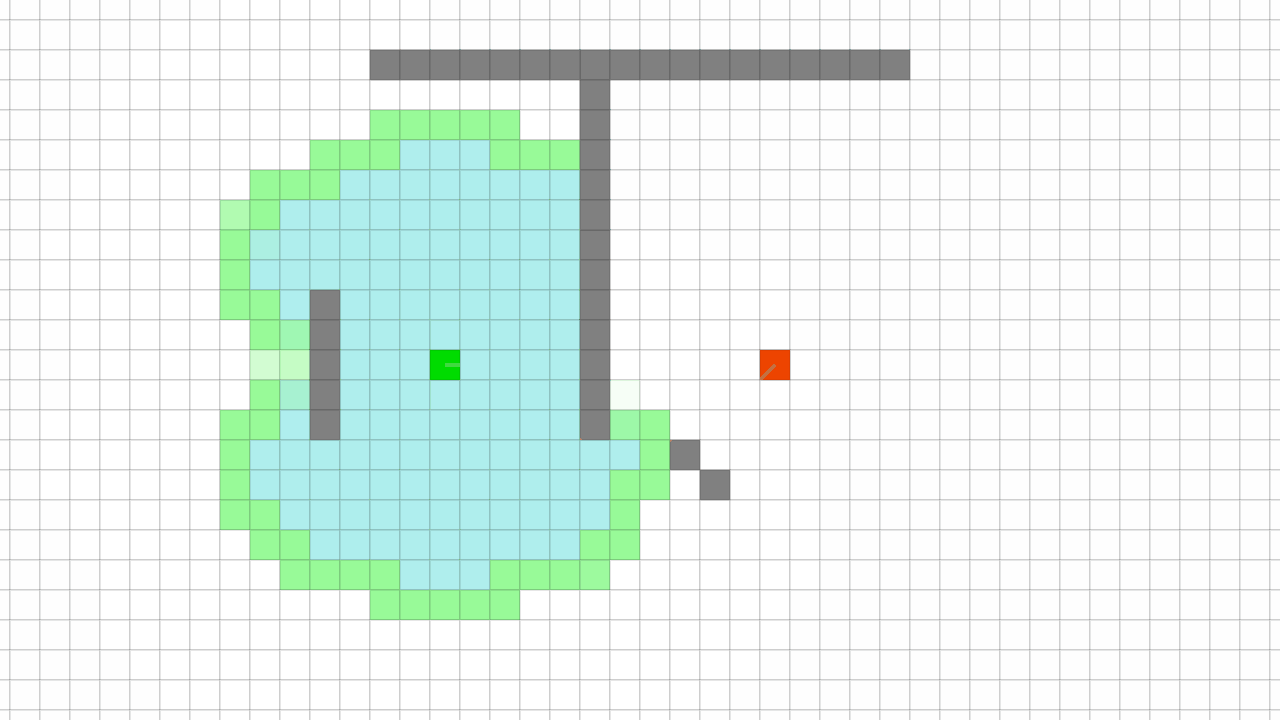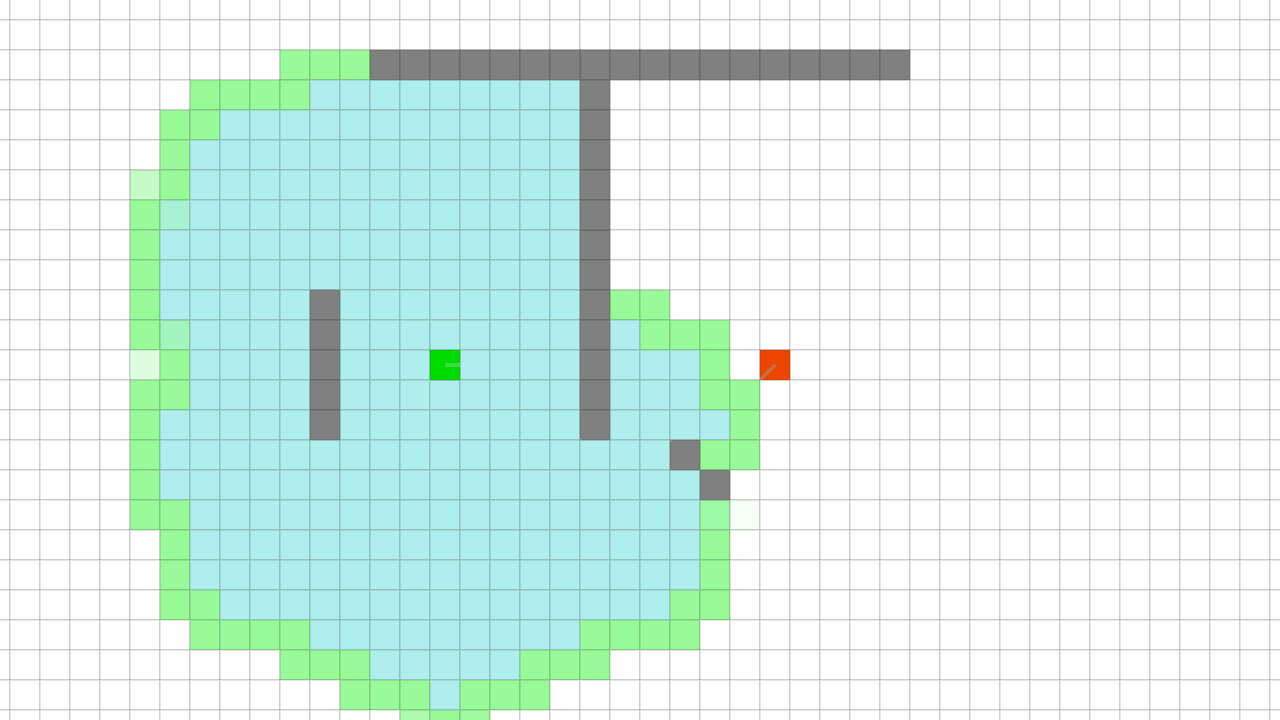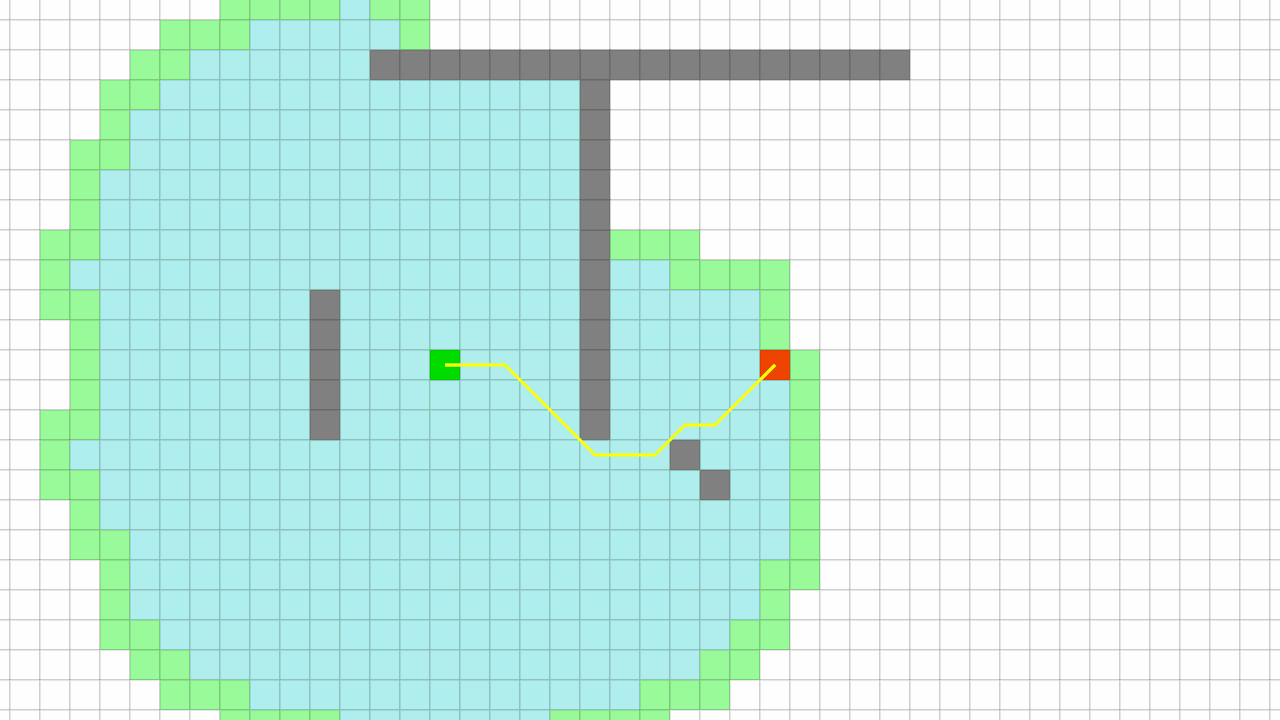
모든 노드에서 길을 찾는 다익지스트라 알고리즘 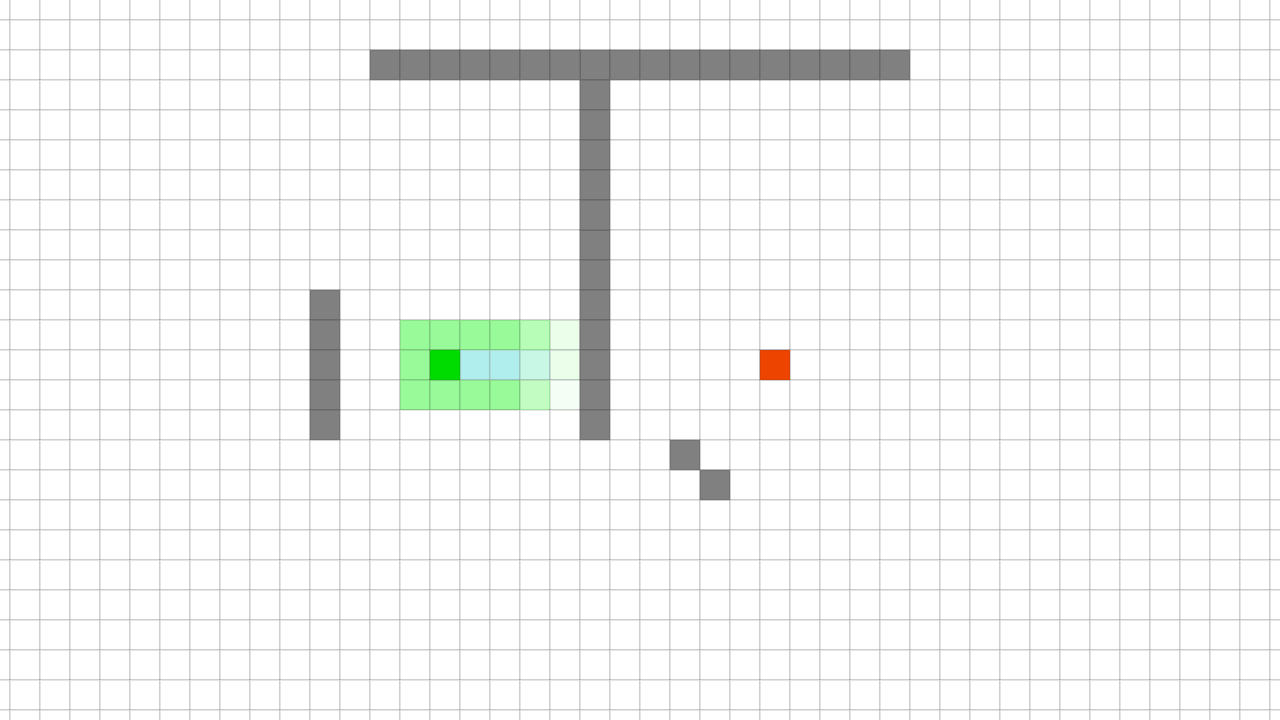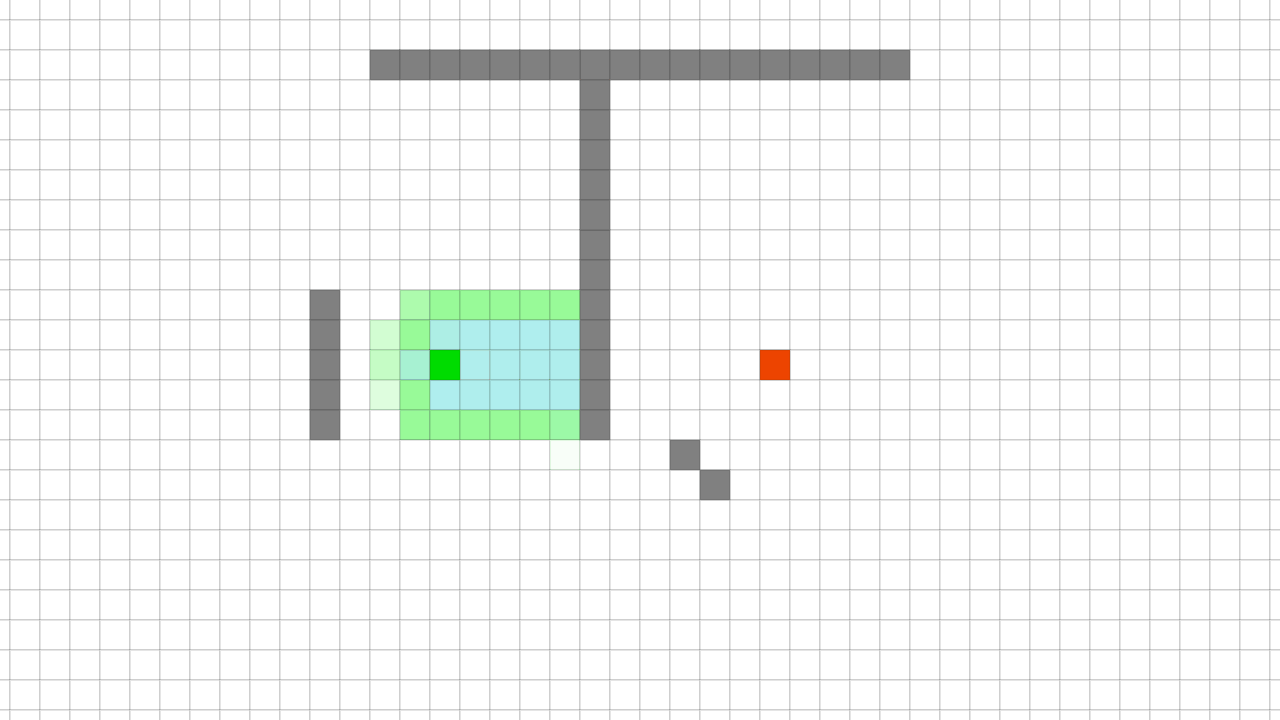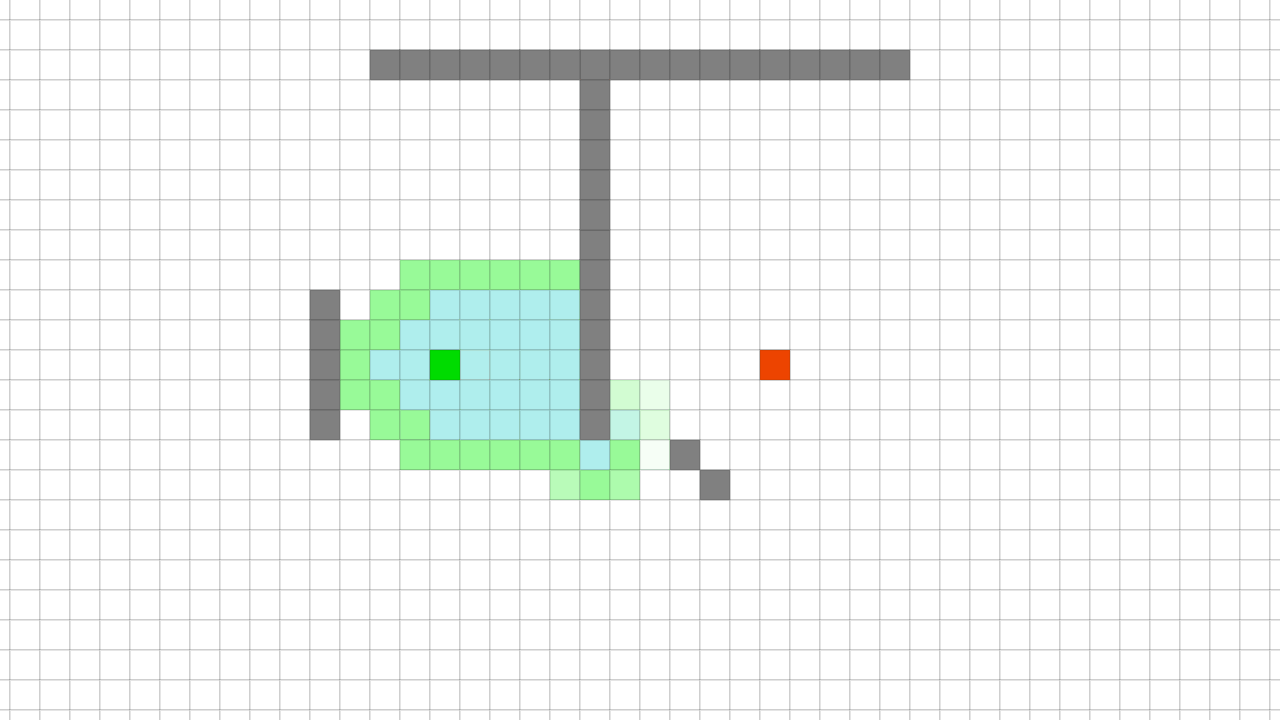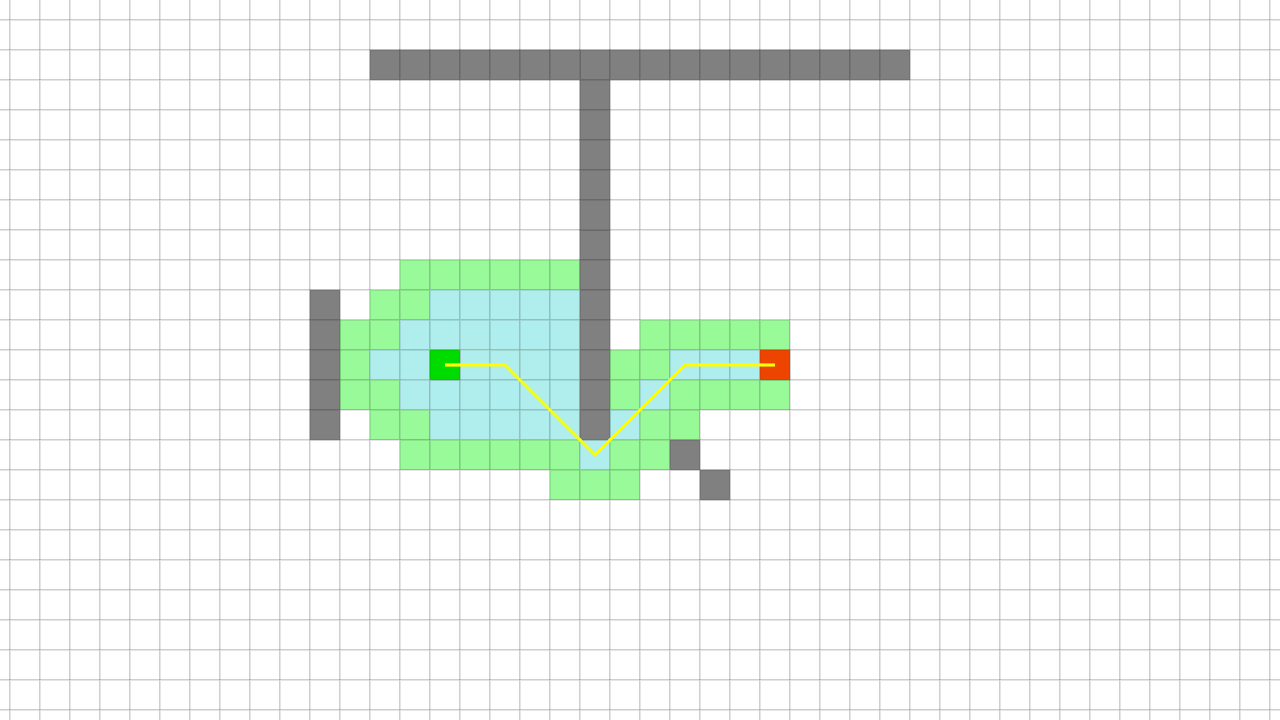
F 값을 이용해, 최선의 노드를 찾아 길을 찾는 A* 알고리즘 Pseudo Code
/* A* 특징 1. openList와 closeList라는 보조 데이터를 사용한다. 2. F = G + H 를 매번 노드를 생성할 때마다 계산한다. 3. openList에는 현재 노드에서 갈 수 있는 노드를 전부 추가해서 F,G,H를 계산한다. openList에 중복된 노드가 있다면, F값이 제일 작은 노드로 바꾼다. 4. closeList에는 openList에서 F값이 가장 작은 노드를 추가시킨다. */ openList.add(startNode) # openList는 시작 노드로 init while openList is not empty: # 현재 노드 = openList에서 F 값 가장 작은 것 currentNode <- node in openList having the lowest F value openList.remove(currentNode) # openList에서 현재 노드 제거 closeList.add(currentNode) # closeList에 현재 노드 추가 if goalNode is currentNode: currentNode.parent.position 계속 추가 후 경로 출력 후 종료 children <- currentNode와 인접한 모든 노드 추가 for each child in children: if child in closeList: continue child.g = currentNode.g + child와 currentNode 거리(1) child.h = child와 목적지까지의 거리 child.f = child.g + child.h # child가 openList에 있고, child의 g 값이 openList에 중복된 노드 g값과 같으면 # 다른 자식 불러오기 if child in openList and child.g > openNode.g in openList: continue openList.add(child)파이썬
길을 바꿔가며 테스트해본다.
더보기# Time Complexity는 H에 따라 다르다. # O(b^d), where d = depth, b = 각 노드의 하위 요소 수 # heapque를 이용하면 길을 출력할 때 reverse를 안해도 됨 import heapq # priority queue class Node: def __init__(self, parent=None, position=None): self.parent = parent self.position = position self.g = 0 self.h = 0 self.f = 0 def __eq__(self, other): return self.position == other.position def __lt__(self, other): return self.f < other.f def heuristic(node, goal, D=1, D2=2 ** 0.5): # Diagonal Distance dx = abs(node.position[0] - goal.position[0]) dy = abs(node.position[1] - goal.position[1]) return D * (dx + dy) + (D2 - 2 * D) * min(dx, dy) def aStar(maze, start, end): # startNode와 endNode 초기화 startNode = Node(None, start) endNode = Node(None, end) # openList, closedList 초기화 openList = [] closedSet = set() # openList에 시작 노드 추가 heapq.heappush(openList, startNode) # endNode를 찾을 때까지 실행 while openList: # 현재 노드 지정 currentNode = heapq.heappop(openList) closedSet.add(currentNode.position) # 현재 노드가 목적지면 current.position 추가하고 # current의 부모로 이동 if currentNode == endNode: path = [] while currentNode is not None: path.append(currentNode.position) currentNode = currentNode.parent return path[::-1] # 인접한 xy좌표 전부, DFS for newPosition in (0, -1), (0, 1), (-1, 0), (1, 0), (-1, -1), (-1, 1), (1, -1), (1, 1): # 노드 위치 업데이트 nodePosition = (currentNode.position[0] + newPosition[0], currentNode.position[1] + newPosition[1]) # 미로 maze index 범위 안에 있어야함 if nodePosition[0] > len(maze) - 1 or nodePosition[0] < 0 or nodePosition[1] > len(maze[0]) - 1 or nodePosition[1] < 0: continue # 장애물이 있으면 다른 위치 불러오기 if maze[nodePosition[0]][nodePosition[1]] != 0: continue new_node = Node(currentNode, nodePosition) # 자식이 closedList에 있으면 continue if new_node.position in closedSet: continue # f, g, h값 업데이트 new_node.g = currentNode.g + 1 new_node.h = heuristic(new_node, endNode) new_node.f = new_node.g + new_node.h # 자식이 openList에 있으고, g값이 더 크면 continue # new_node.g >= child.g 로 하면 openList 중복성을 줄일 수도 있습니다. # 하지만 이건 시나리오에 따라 다르고, 대부분 엄격히 더 낮은 g 값을 확인하면 충분할 수 있습니다. if any(child for child in openList if new_node == child and new_node.g > child.g): continue heapq.heappush(openList, new_node) def main(): maze = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]] start = (0, 0) end = (7, 6) path = aStar(maze, start, end) print(path) if __name__ == '__main__': main() # [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 3), (5, 4), (6, 5), (7, 6)] # 실행 시간 : 0.0013초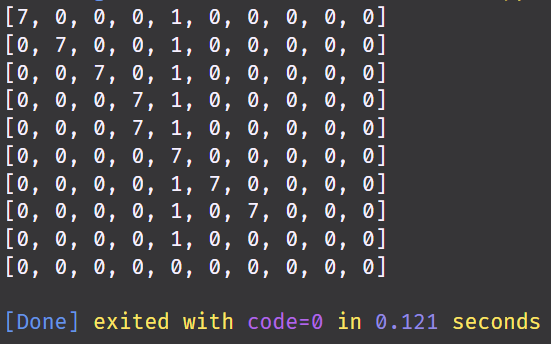
7 = 길 참고 지식 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A*_search_algorithm
참고 이미지 : https://qiao.github.io/PathFinding.js/visual/
참고 코드 : https://gist.github.com/Nicholas-Swift
그래프 표현 최단경로 찾기 (dijikstra) : https://choiseokwon.tistory.com/171?category=247927
728x90'컴퓨터 > 파이썬' 카테고리의 다른 글
Docker + Flask 튜토리얼 (0) 2020.07.30 파이썬 Introspective Sort (내성 정렬) 알고리즘 (0) 2020.07.17 파이썬 array.sort(), TimSort 알고리즘 (1) 2020.07.16